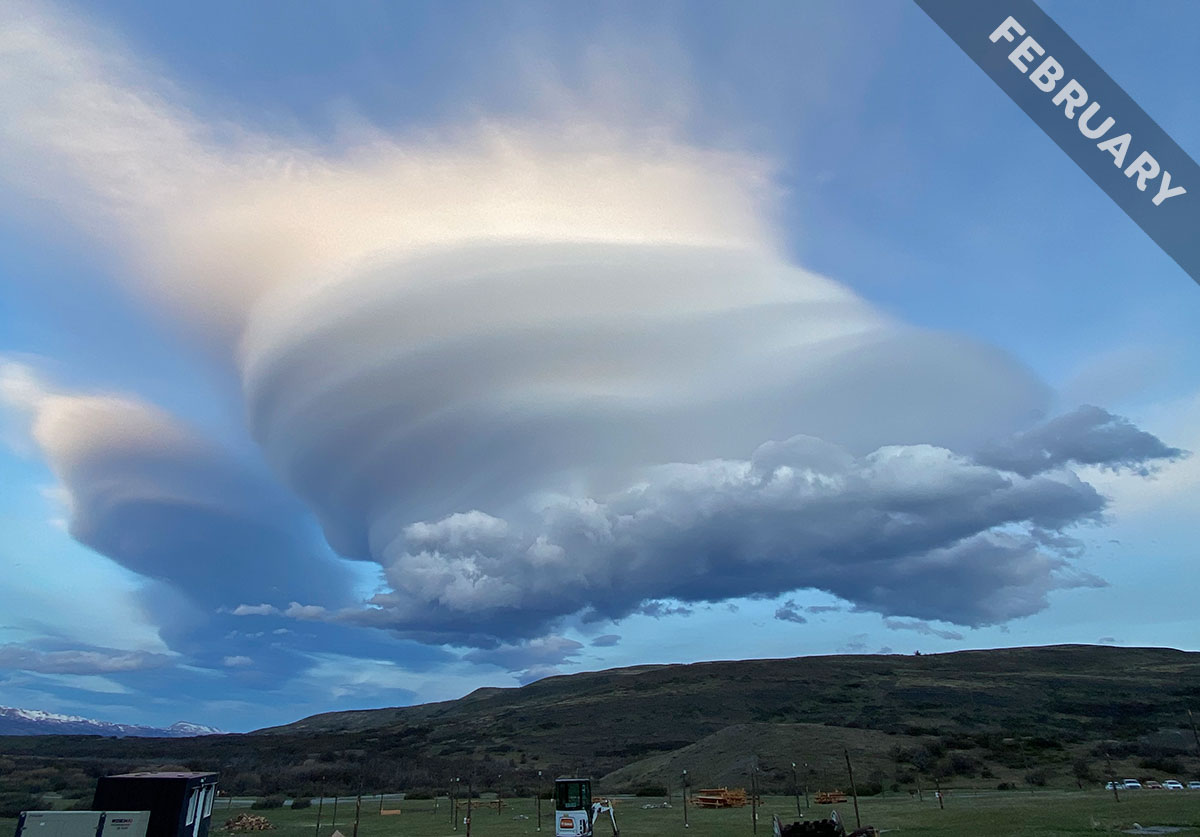
The flow of moist air over mountains can give rise to two very different forms of cloud. Meet the smooth lenticularis cloud and the rough rotor cloud, captured over Patagonia, Chile in February’s Cloud of the Month…
Category: Cloud of the Month
Every month, we choose one of our favourite photographs from the Cloud Gallery to become our Cloud of the Month.
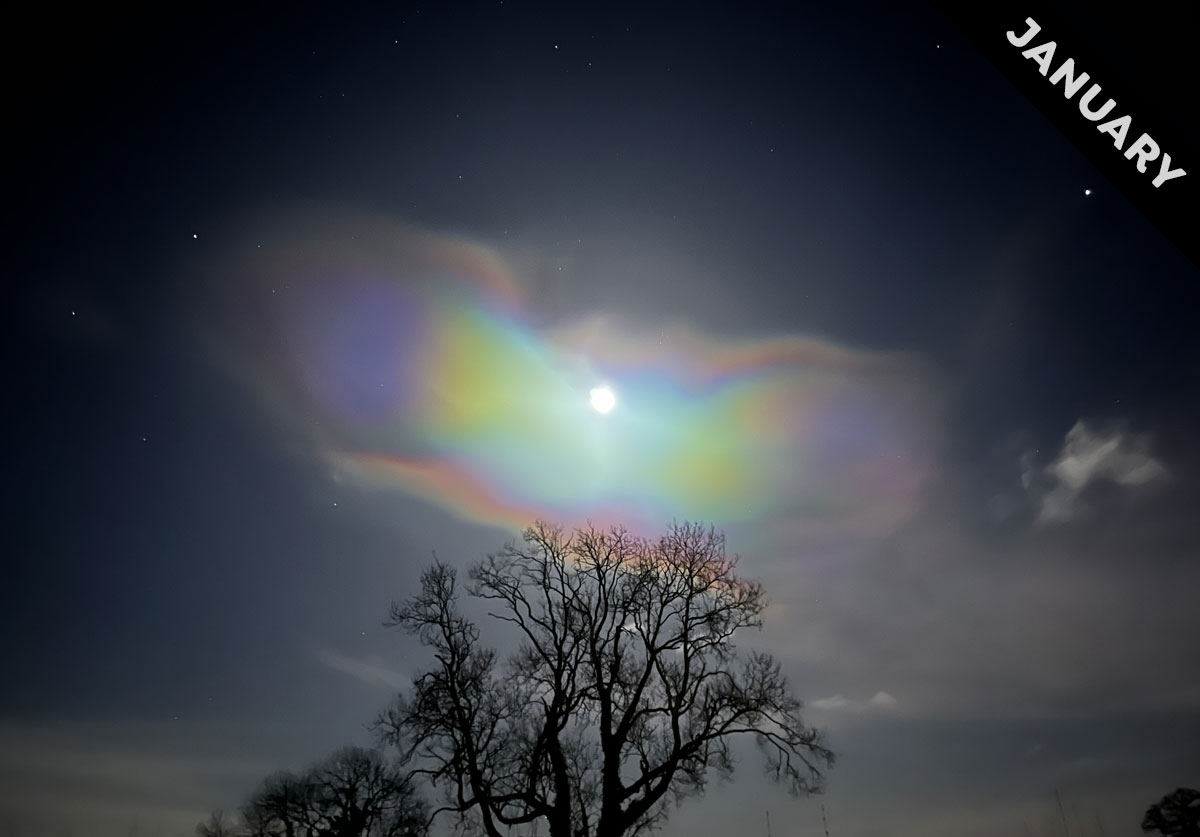
When is the rare, extreme altitude, nacreous cloud even rarer than usual? Find out in Cloud of the Month for January…
Burketown in northern Queensland, Australia has a cloud visitor, known locally as the Morning Glory cloud, which glider pilots surf like the atmospheric equivalent of regular surfers on an ocean wave…
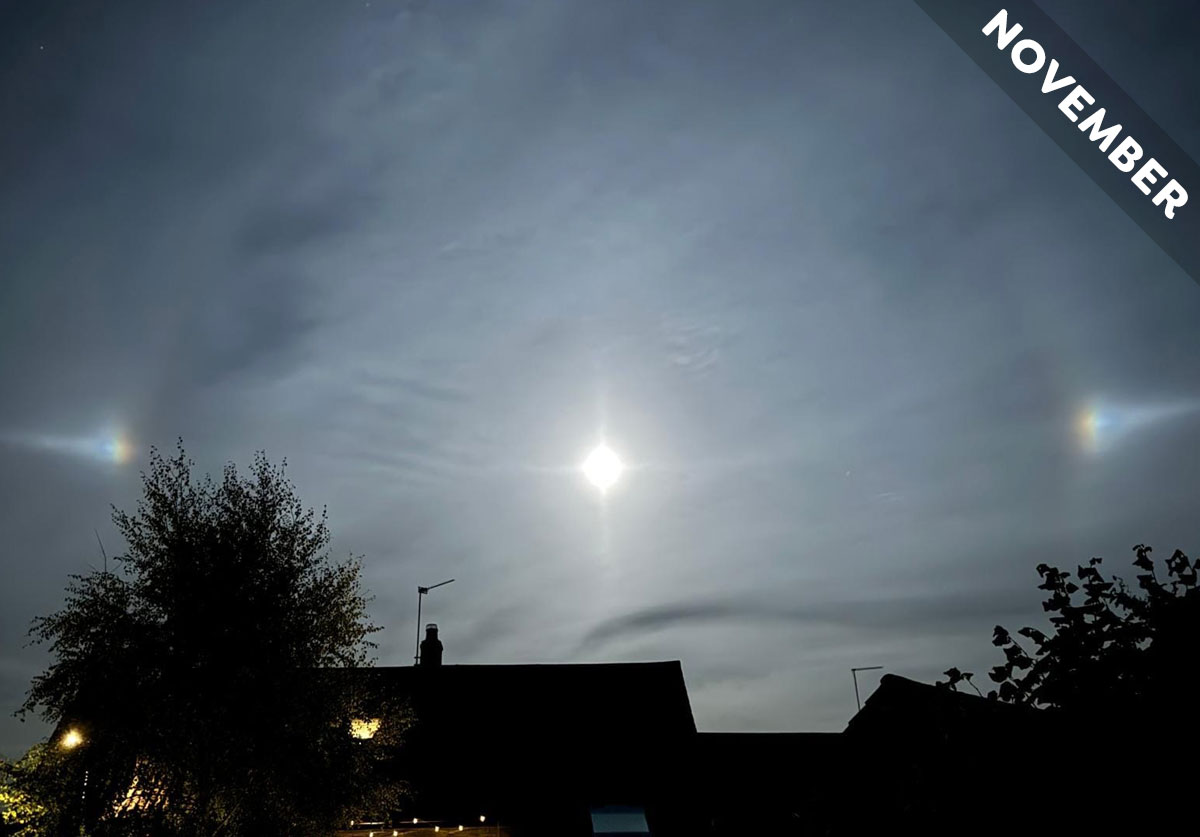
Meet the optical effects that are the Moon’s best friend, in Cloud of the Month for November…
The common, but often stunning, undulatus variety of cloud is a gentle reminder that our atmosphere is an ocean of air…
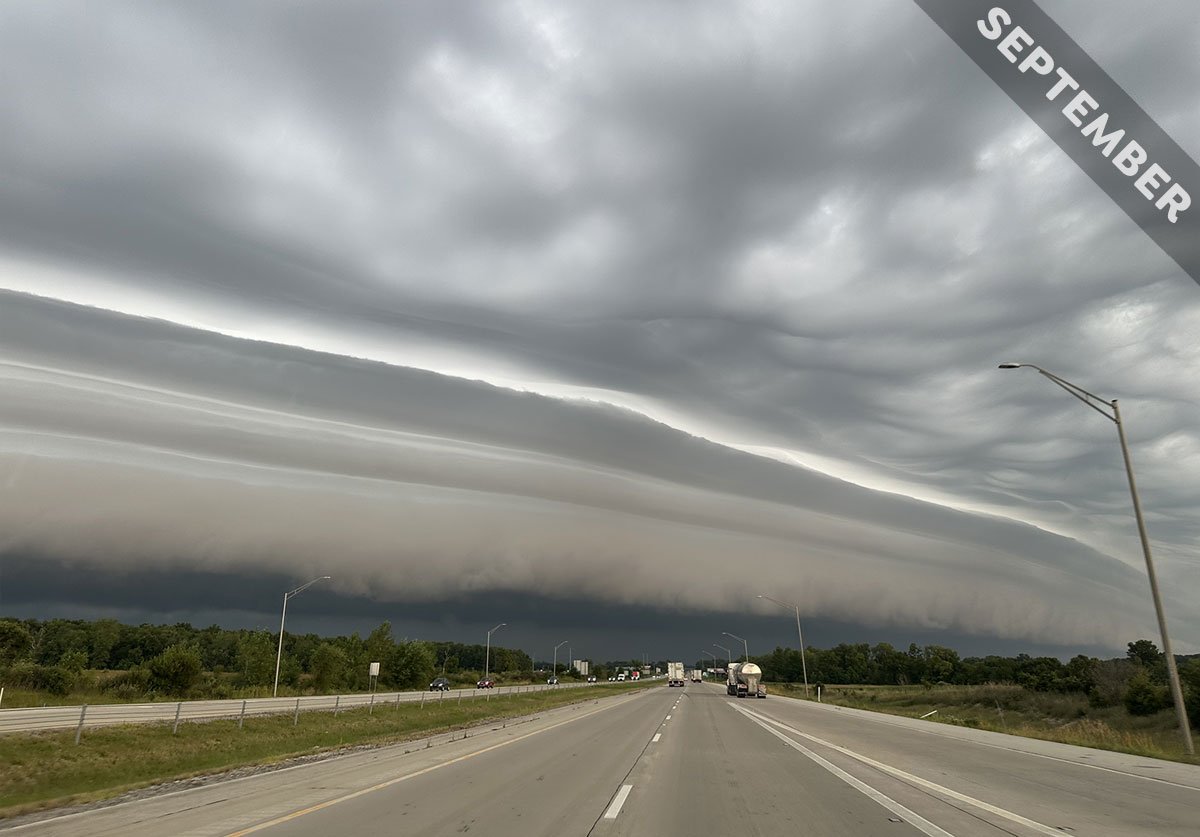
When you see an arcus cloud feature stretching across the sky ahead, you can be sure that heavy showers will soon follow – as we explain in Cloud of the Month for September…
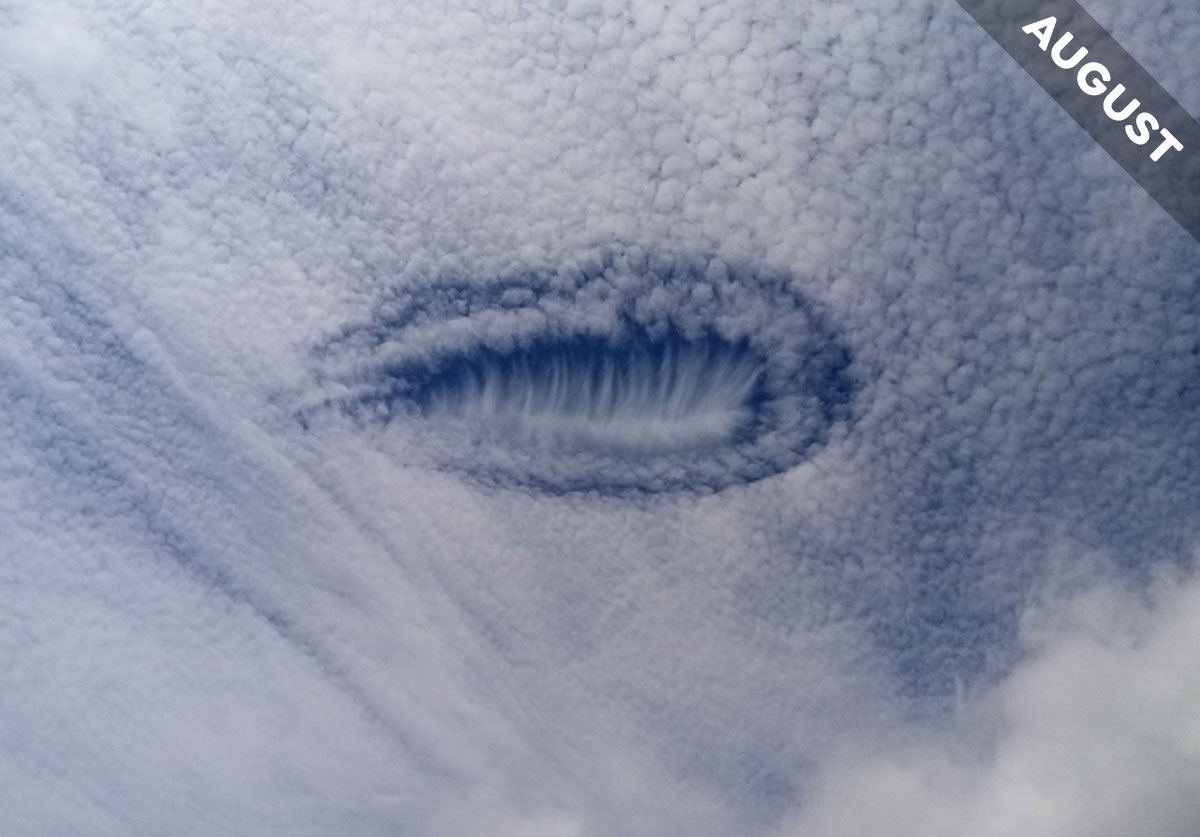
Anne Ducret saw this strange hole in a layer of Altocumulus clouds she spotted over Lot, Occitanie, France. We explain what caused it in Cloud of the Month for August…
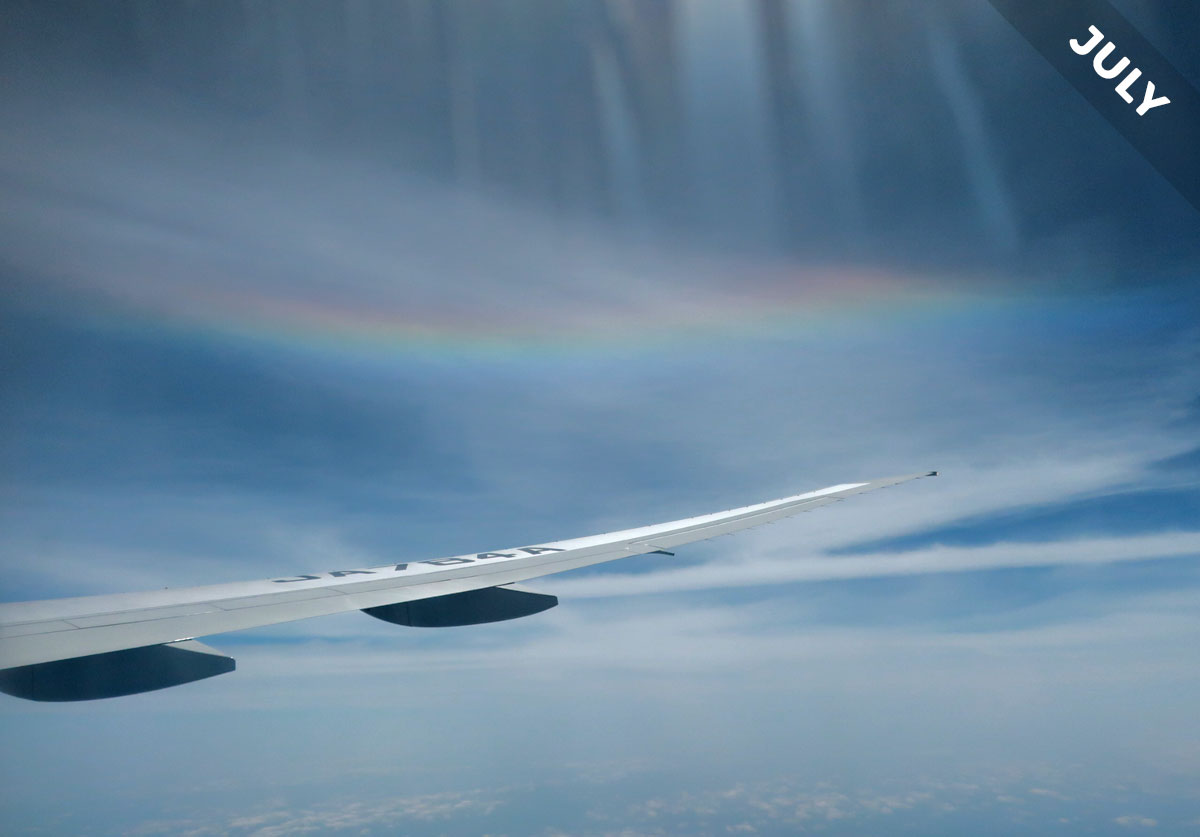
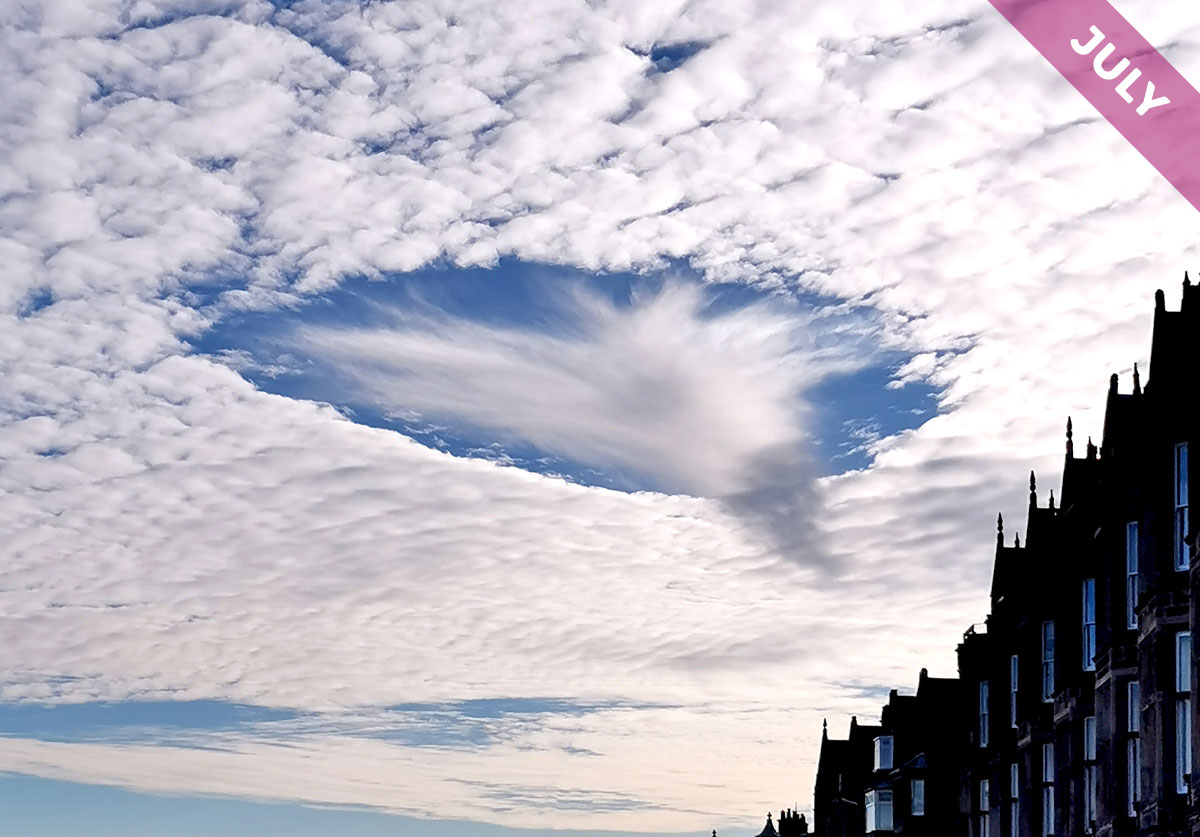
The circumhorizon arc is an optical effect cause by sunlight shining through ice crystals. It looks like a flat rainbow, it forms in the middle of the summer, and it’s Cloud of the Month for July…
Imagine looking up and seeing the sky behave like the underside of a choppy ocean. That’s the dramatic effect of asperitas clouds…
Cloud classifications are mostly based on their appearance. The names typically refer to what the clouds look like. We just say them in Latin to make it feel more official. The lacunosus variety of cloud is a case in point…
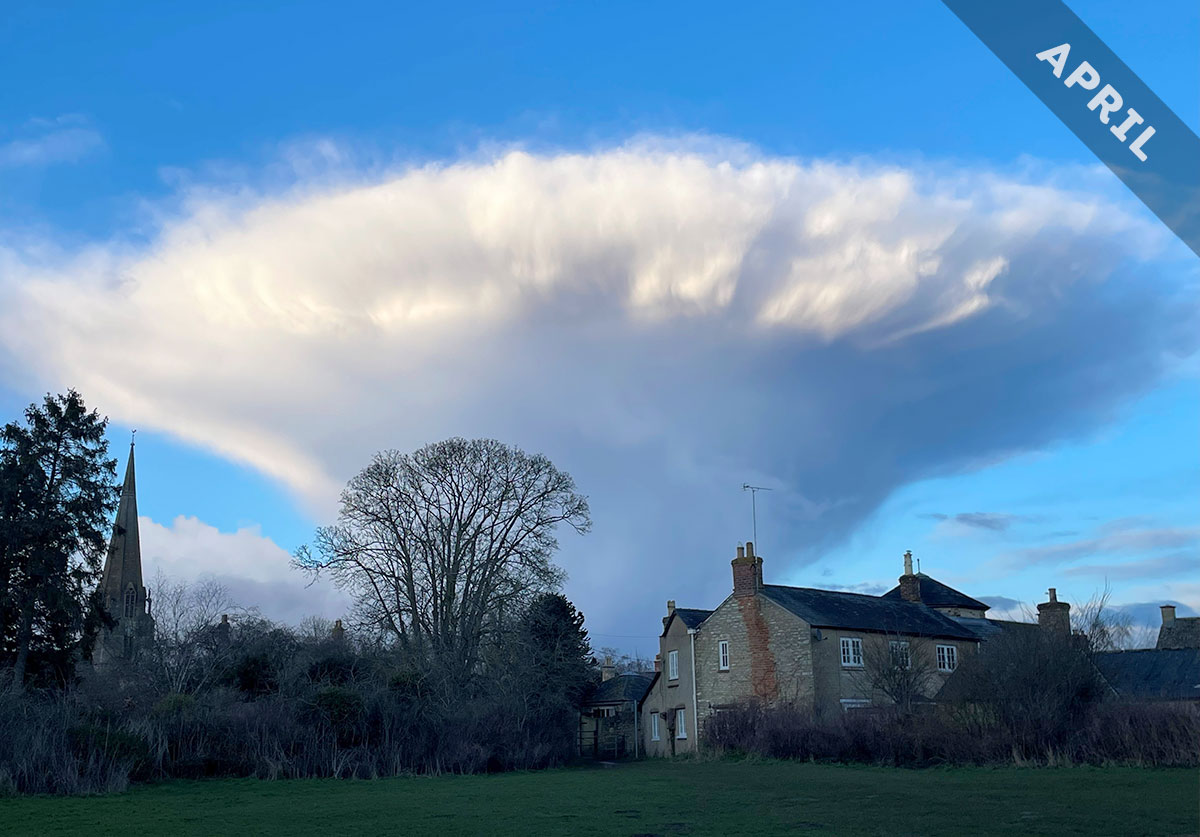
The Cumulonimbus storm cloud is the royalty of the cloud world and it wears a crown of ice, which we have featured as the Cloud of the Month for April…
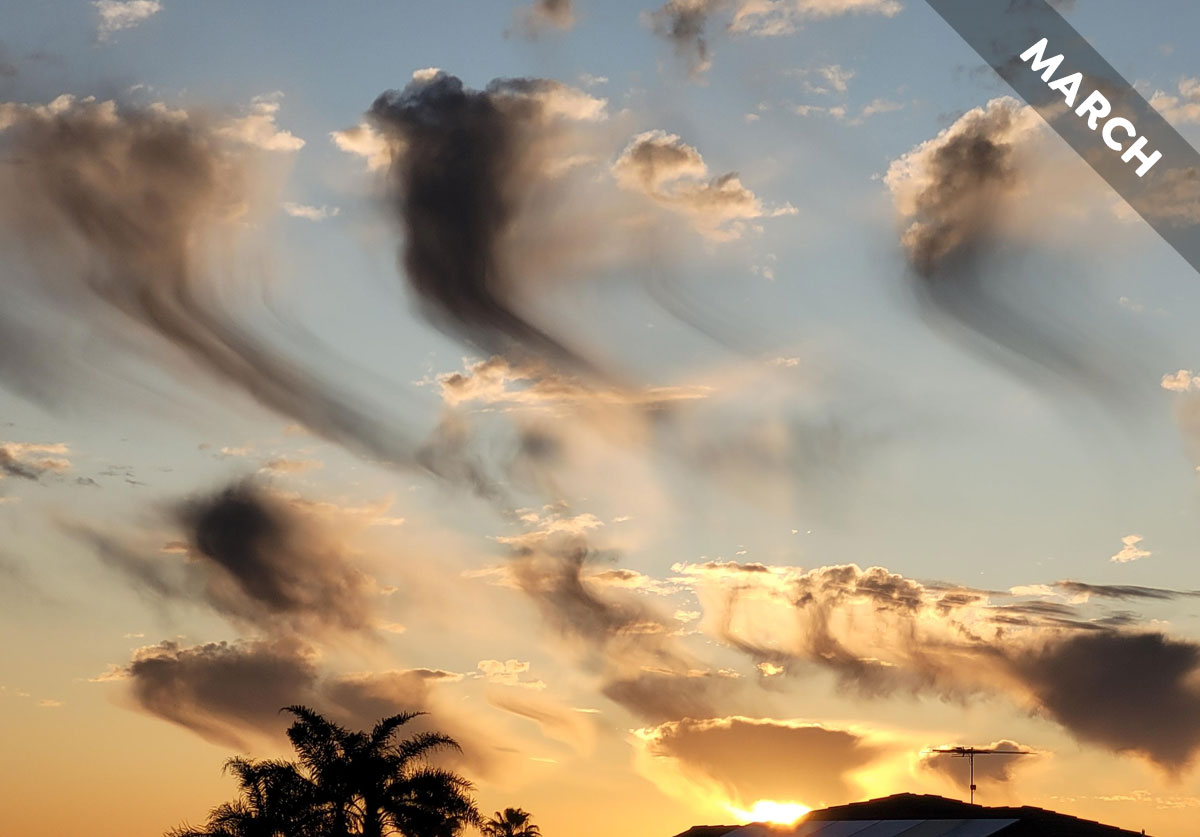
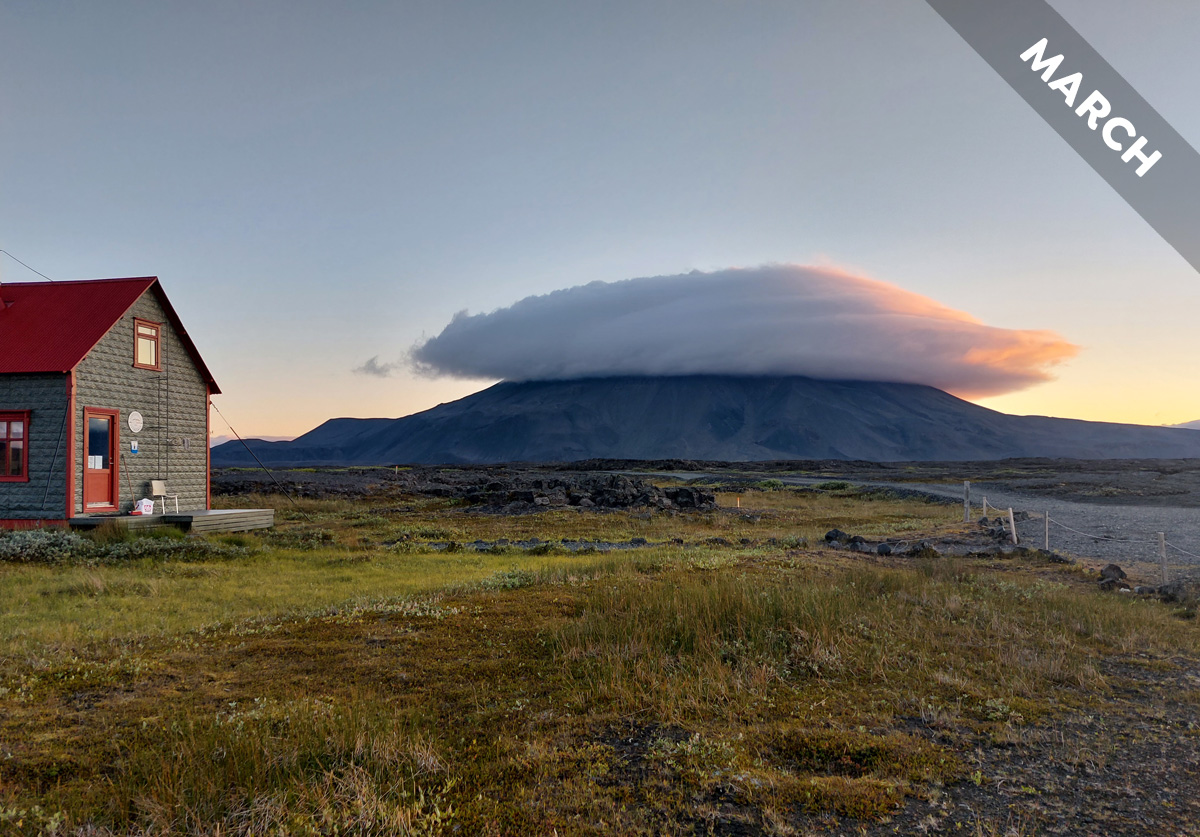
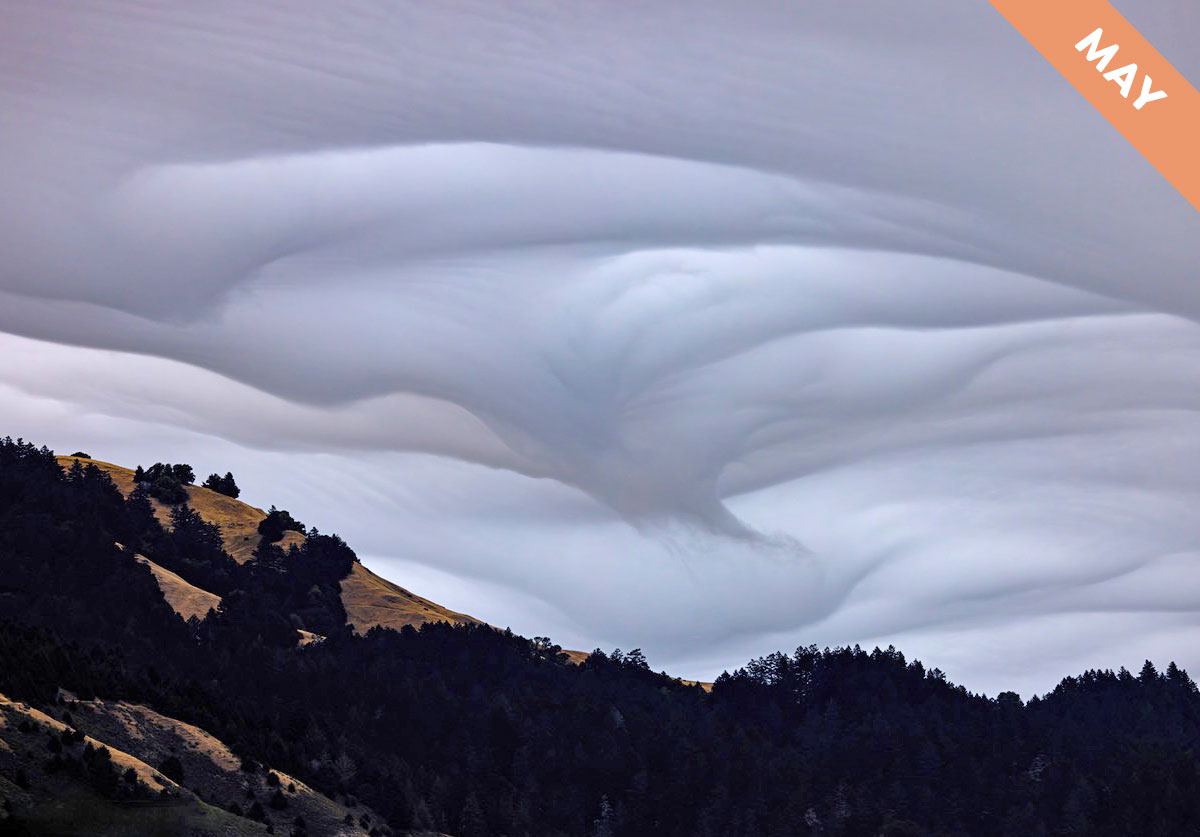
In Cloud of the Month for March, we introduce an atmospheric magic trick…
Cumulus and Altocumulus are like siblings of the cloud family, as we explain in February’s Cloud of the Month…
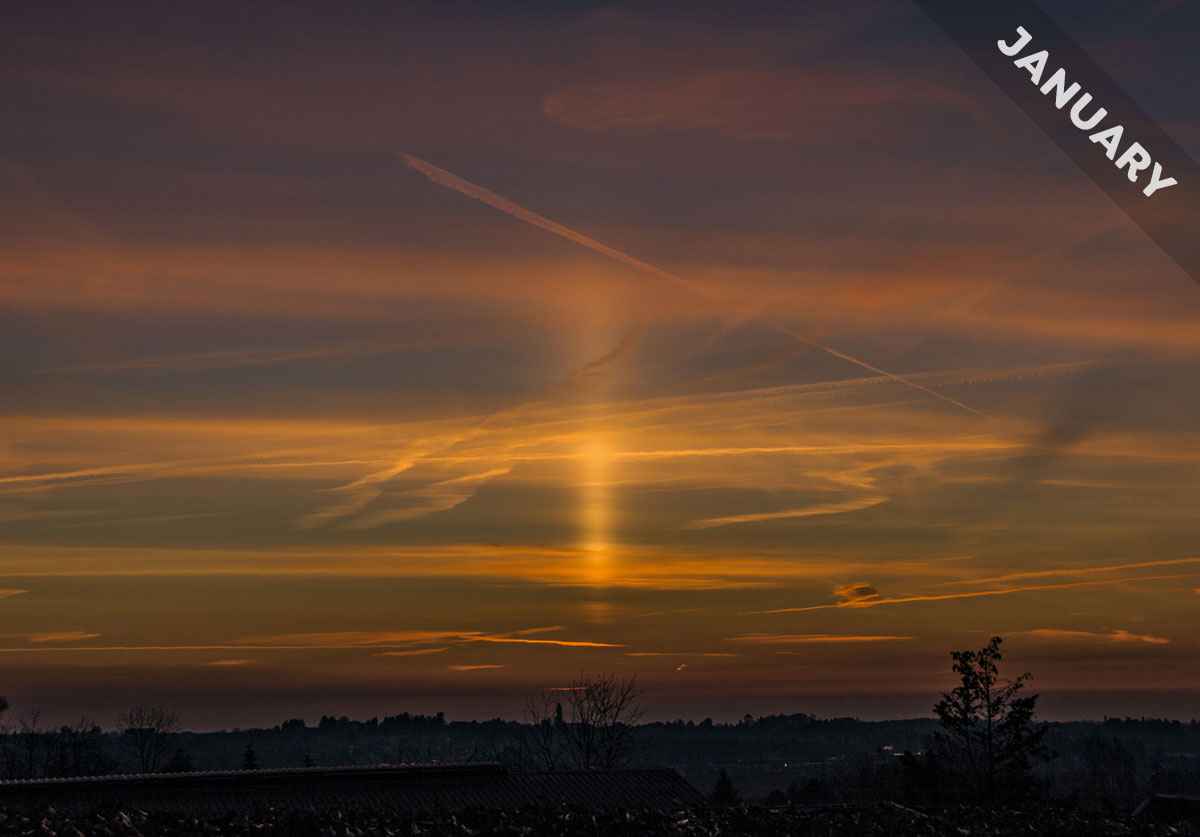
A sun pillar at sunrise heralds the start of a new day in January’s Cloud of the Month…
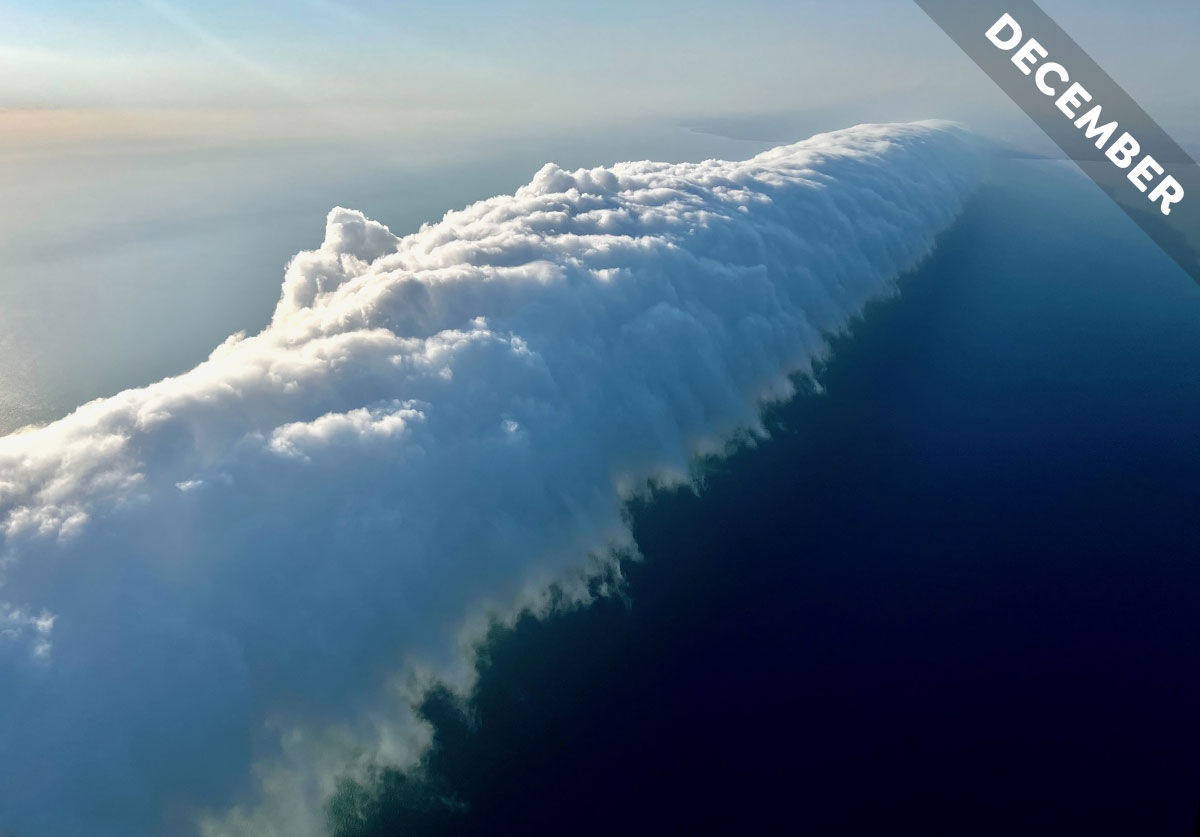
Many optical effects caused by clouds exhibit precise, geometric shapes but not the corona. We embrace this often wonky light effect in Cloud of the Month for December…
Want to learn how to read clouds to forecast the weather? Look for the comma-shaped formations known as Cirrus uncinus that feature as Cloud of the Month for November…
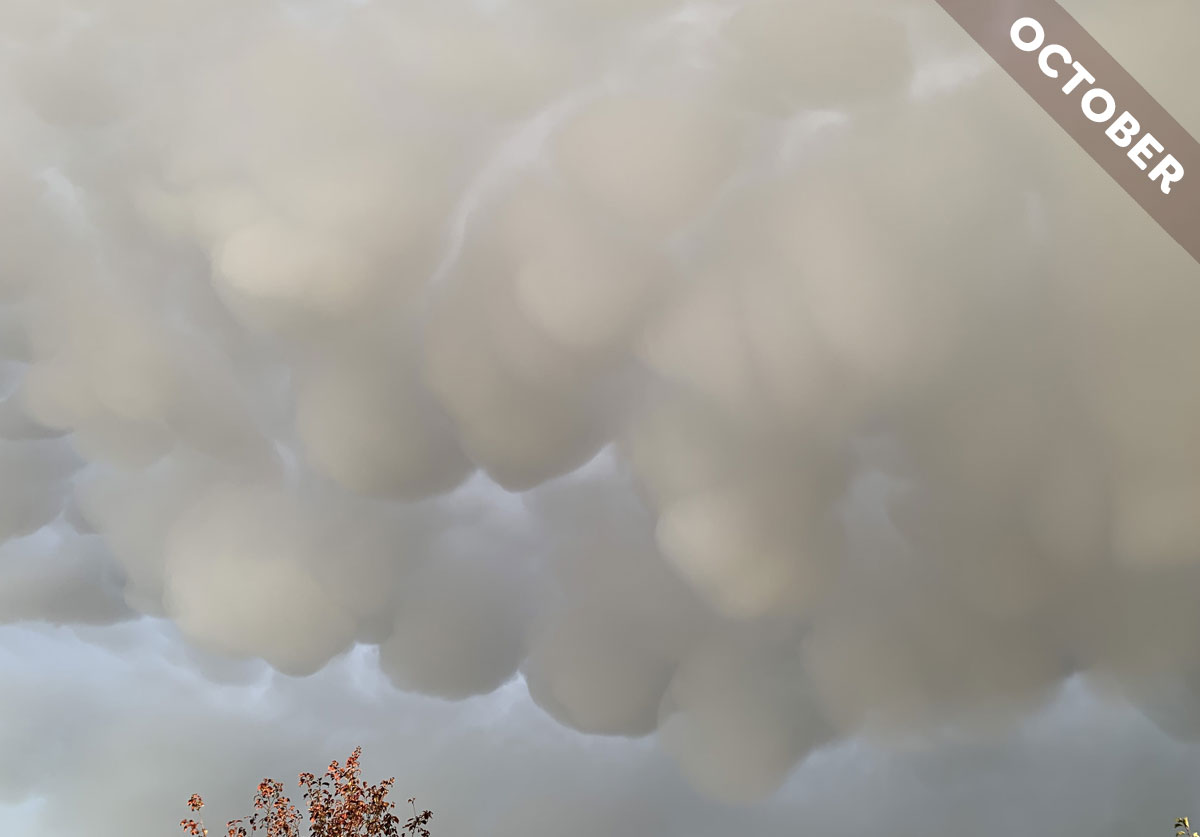
Meet the mother of all storm cloud features, and learn if it tells you that the storm’s heading towards you or away from you, in Cloud of the Month for October…
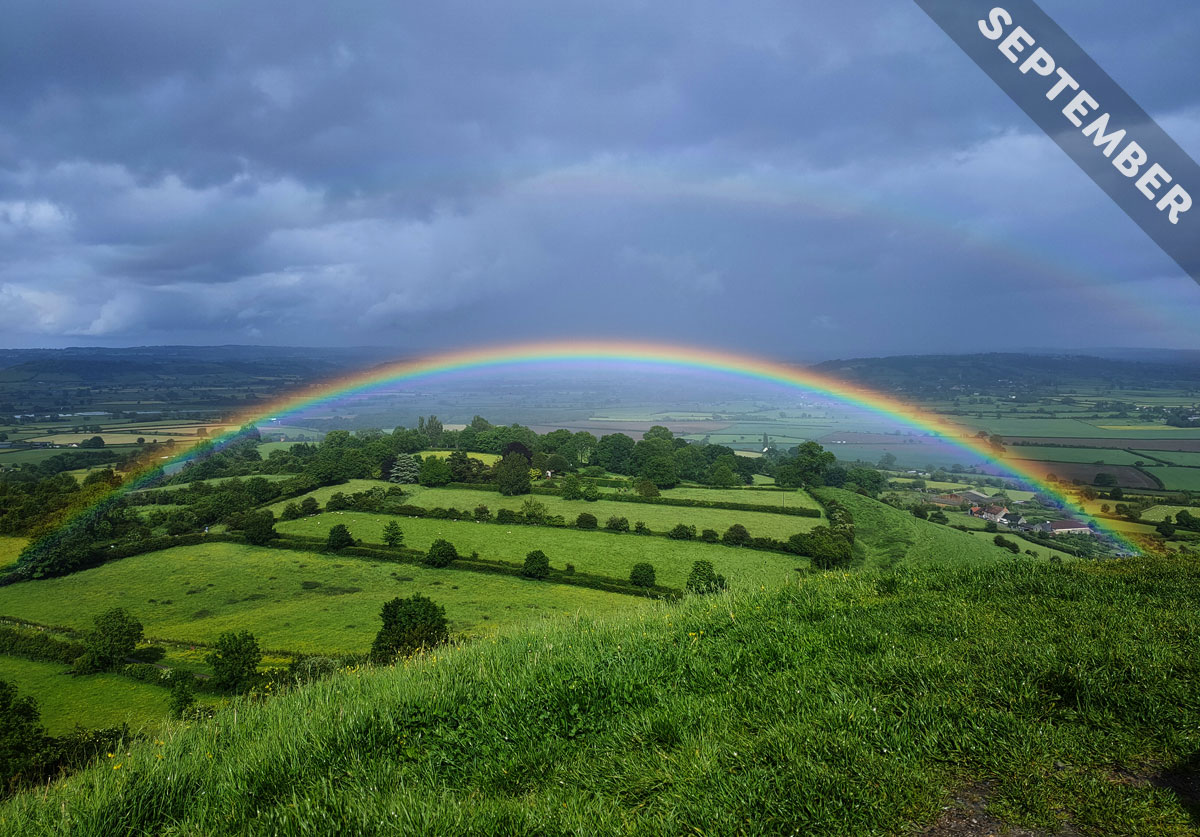
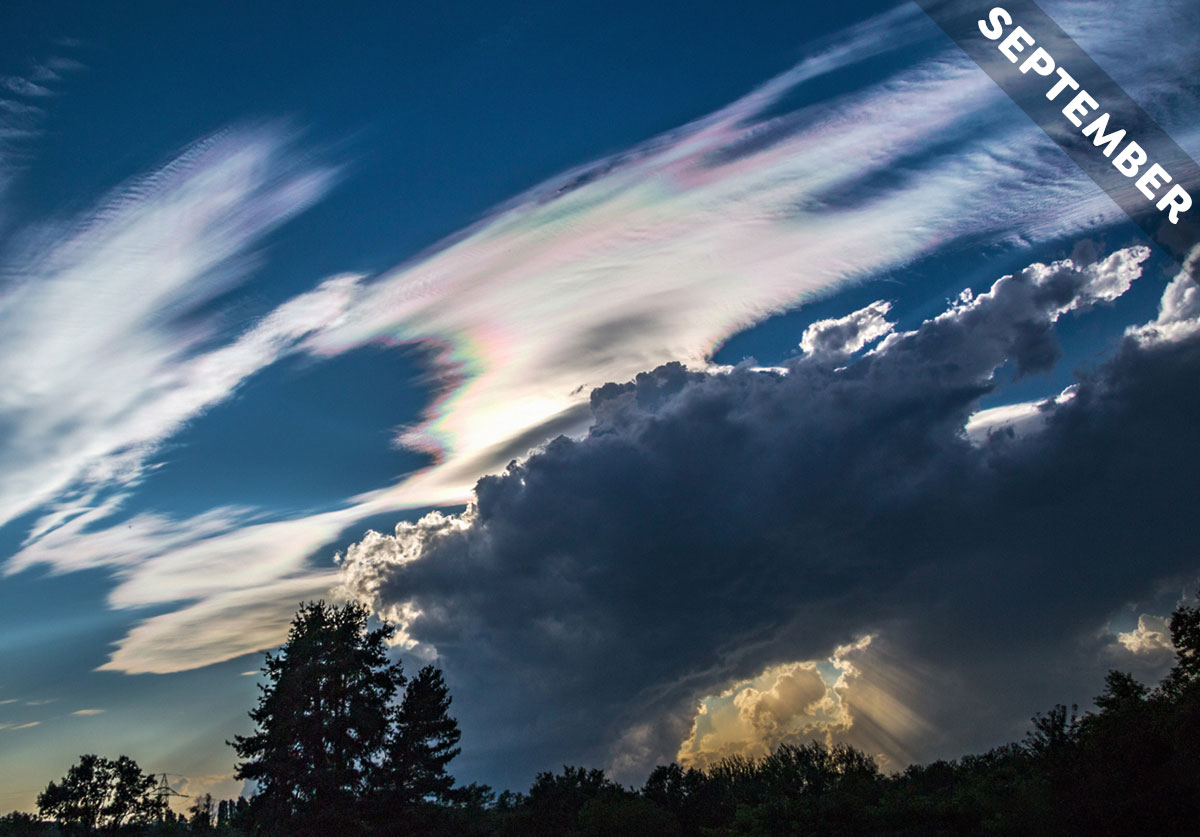
For many cultures, rainbows are symbols of hope. Why is that? We think it comes down to the way a rainbow forms, as we explain in Cloud of the Month for September…
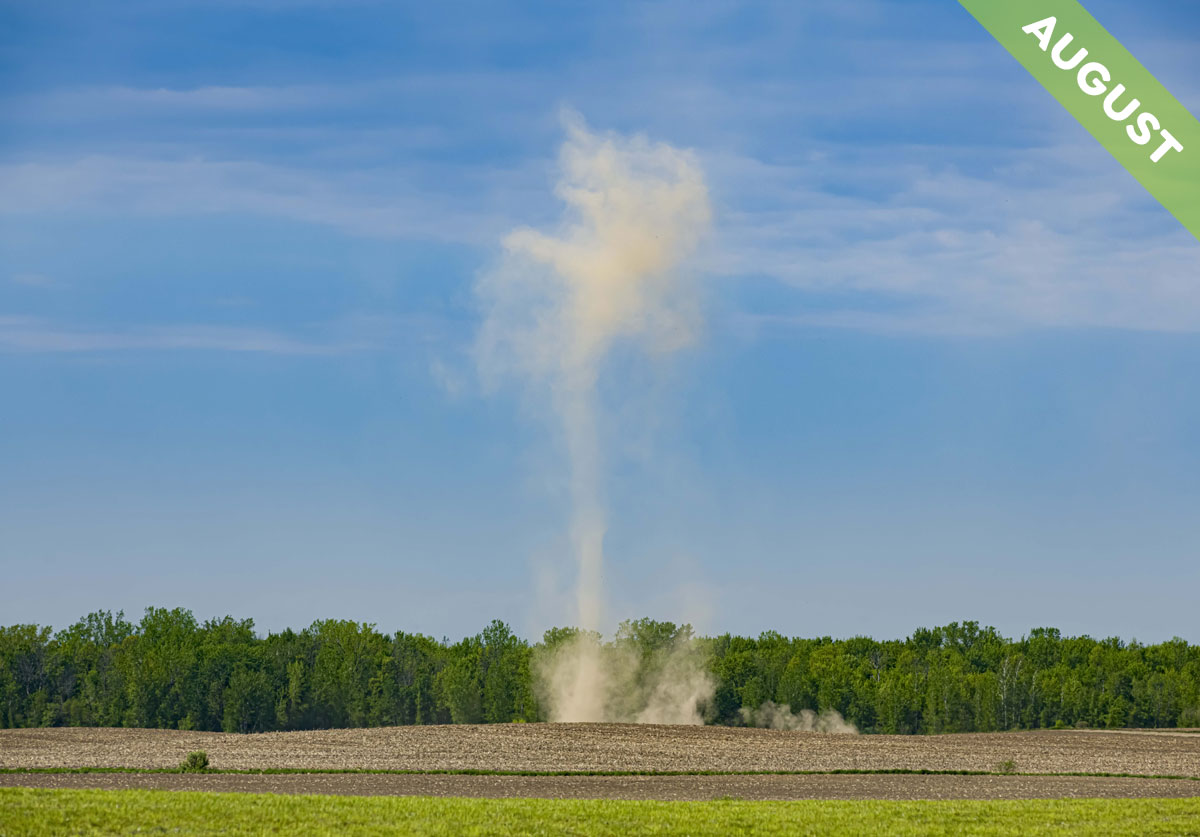
Eyebrow clouds with disco colours! Meet the cloud that deserves an official classification, and which we featured as Cloud of the Month for August…
Meet the highest clouds in our atmosphere. They’re ghostly blue and they shine at night and they feature as Cloud of the Month for July…
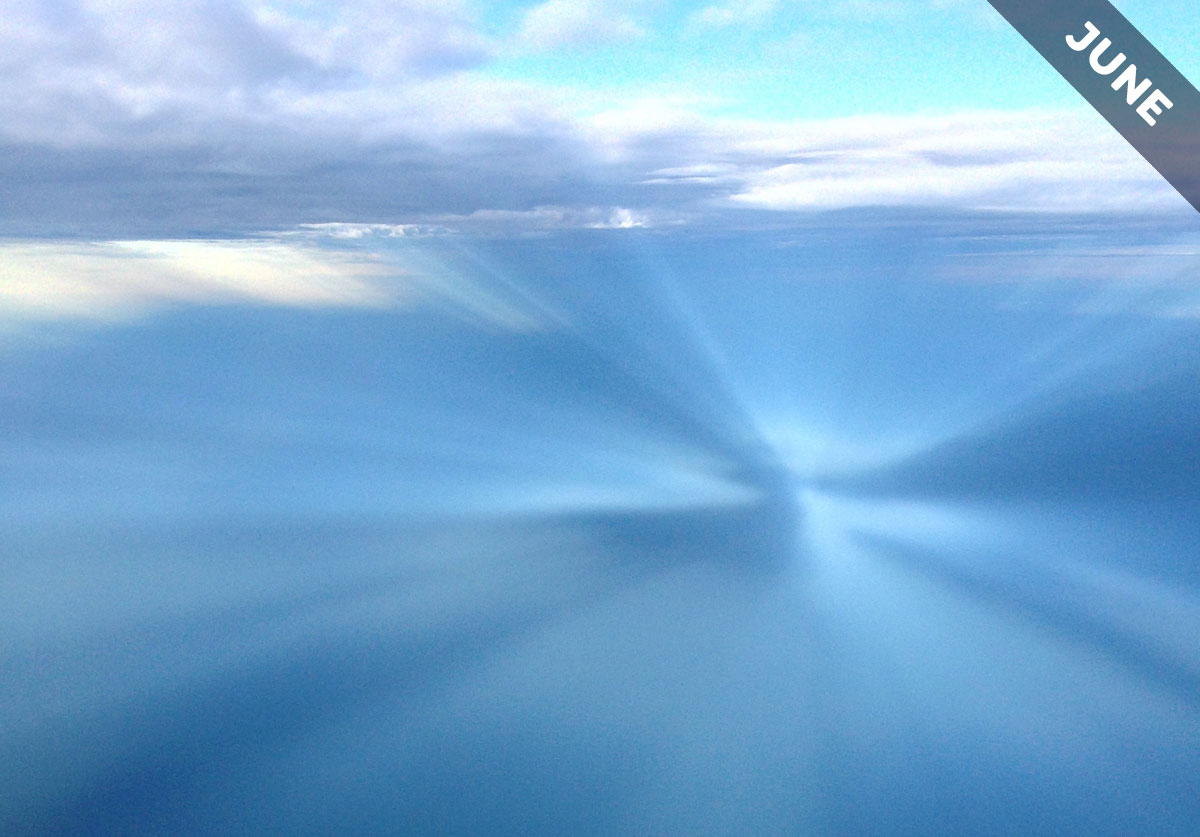
The illusion of perspective is at its most impressive when you observe beams of light and shade, known as anti-crepuscular rays, from the window of an aircraft. That’s why we featured some as Cloud of the Month for June…
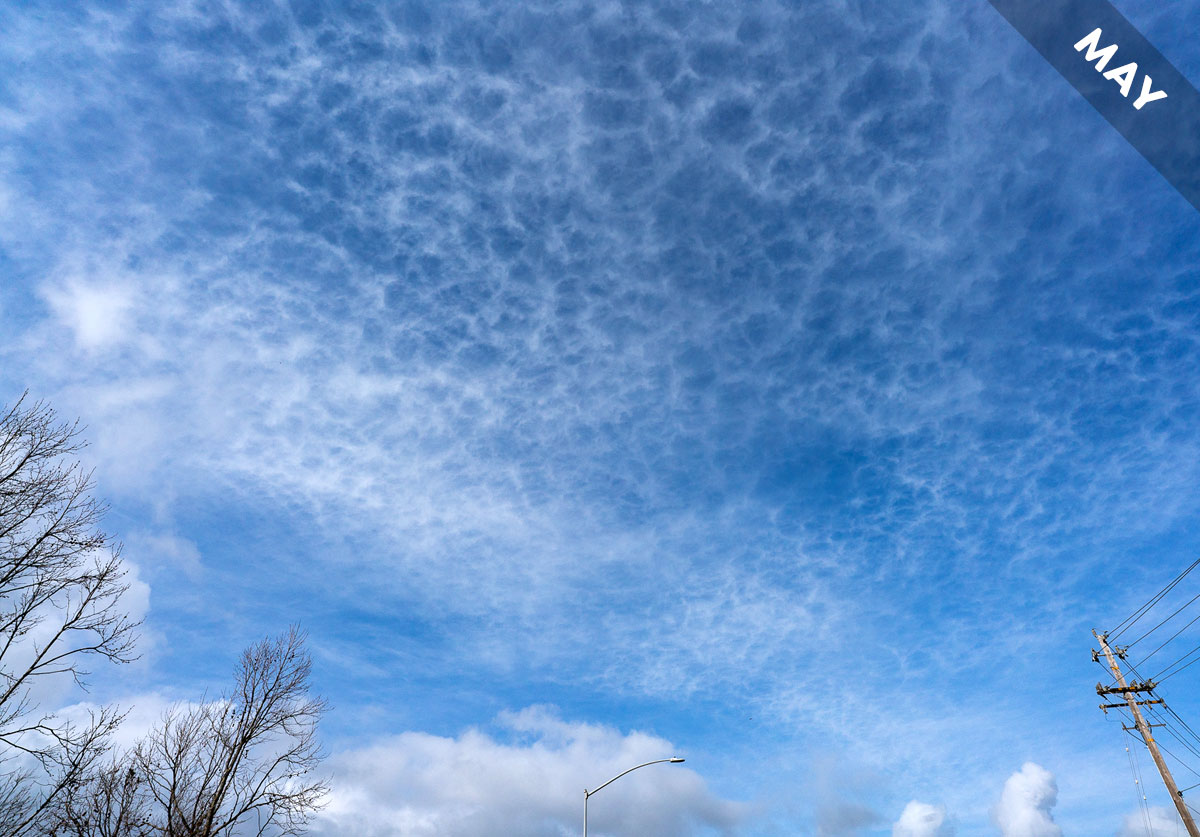
Only one of the ten main types of cloud can produce lightning. Only Cumulonimbus has the superpower to shoot electricity through the air, which is why we’re featuring it as Cloud of the Month for May…
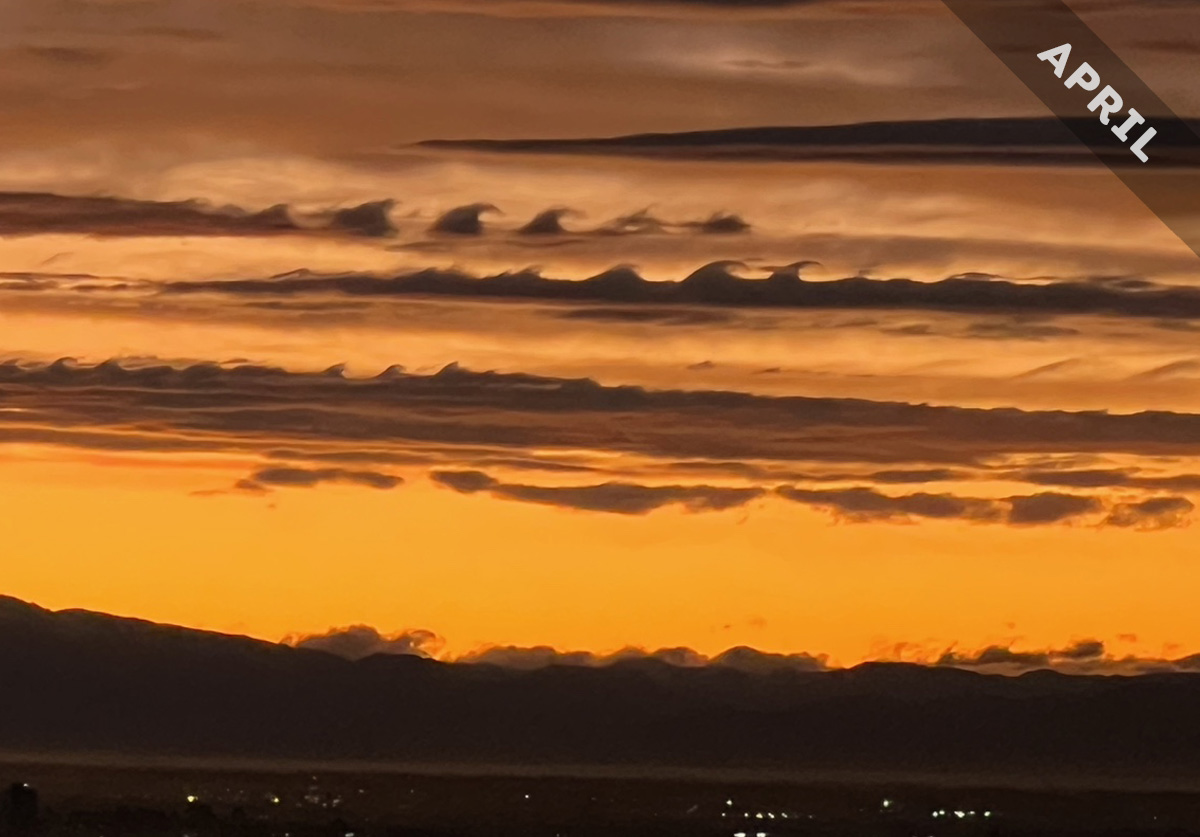
Fluctus is a cloud formed by a particular wind pattern known as wind shear. With its breaking-wave curls, it is the most iconic of all the wave clouds, and it features as Cloud of the Month for April…
It’s this season’s ultimate in mountain fashion. Check out the cap cloud, which we feature as Cloud of the Month for March…
Ever wondered how low a low cloud can go? In Cloud of the Month for February, we introduce you to the blanket of cloud that can form right down at the ground and fill mountain valleys to the brim…
Last month saw the most dramatic display over Europe in over 15 years of the most colourful cloud in our skies. We explain all in Cloud of the Month for January…
Spotting a dramatic display of ice-crystal optical effects is about being in the right place, at the right time, with the right cloud…
Meet the cloud that glider pilots surf like an ocean wave…
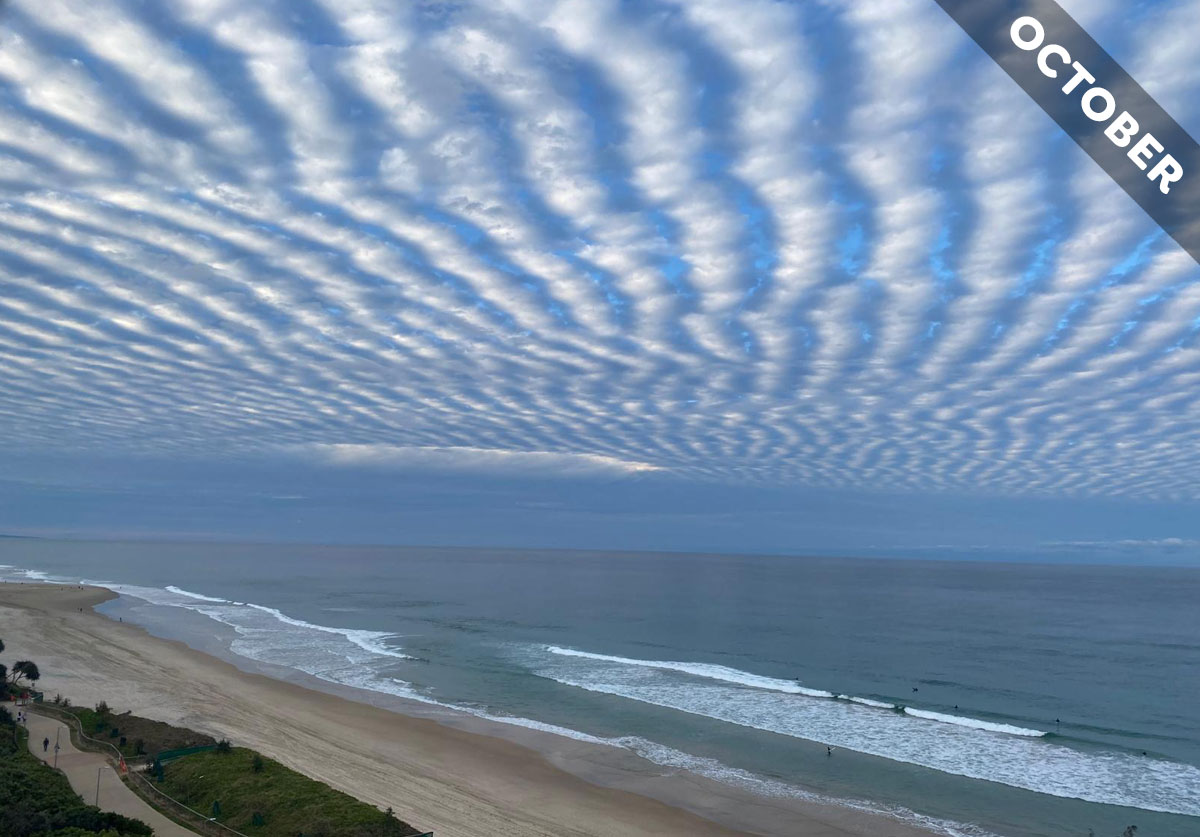
Cirrocumulus usually appears in patches that don’t hang around for long. October’s Cloud of the Month shows an unusually rare expansive form of this fleeting cloud…
What makes a cloud turn multicoloured? We explain in September’s Cloud of the Month…
On a hot, still day in the height of summer, a spinning cloud of dust can develop. It’s known as a dust devil, and it features as a very dry Cloud of the Month for August…
A cavum, or fallstreak hole, is the perfect cloud feature for any clouspotter with a sweet tooth, as we explain in Cloud of the Month for July…
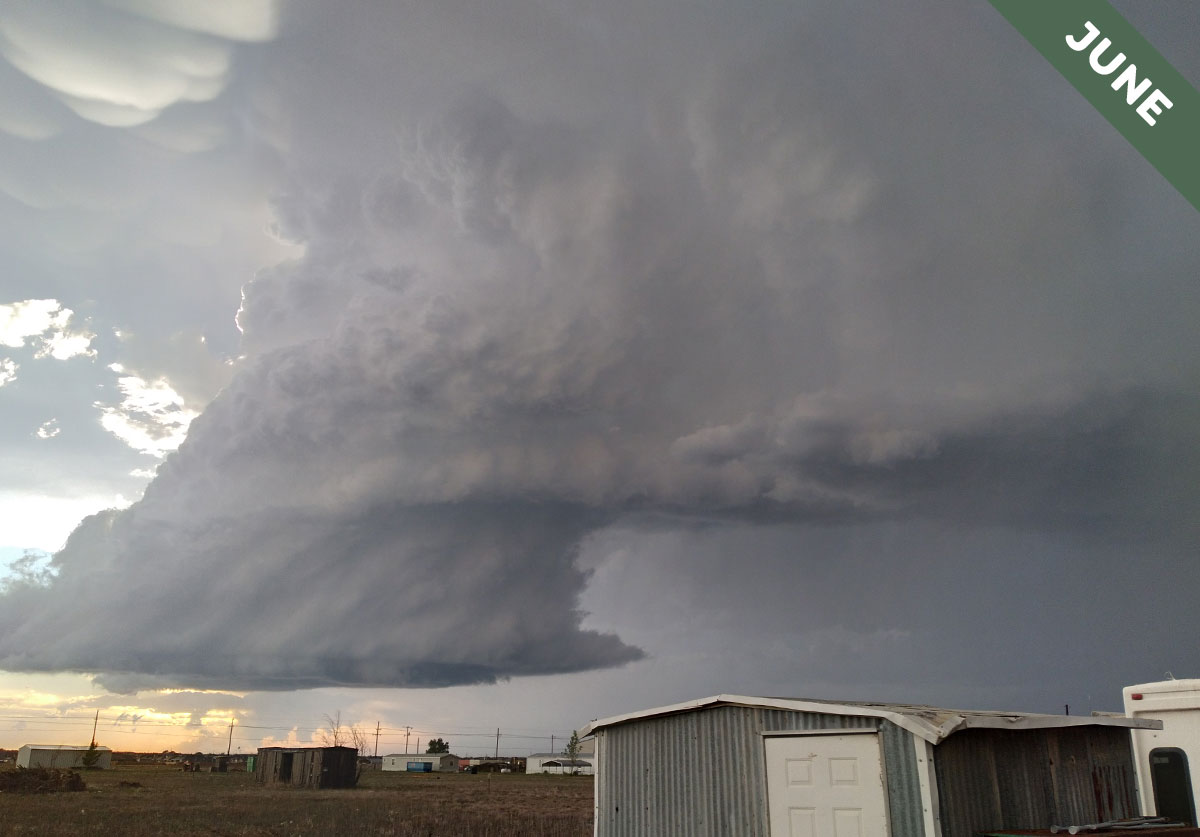
In Cloud of the Month for June, we introduce the murus cloud, which appears beneath huge storm systems and likes to give birth to tornadoes…
When the sky imitates a turbulent sea and giant meringue peaks, you’re likely looking at an asperitas cloud…
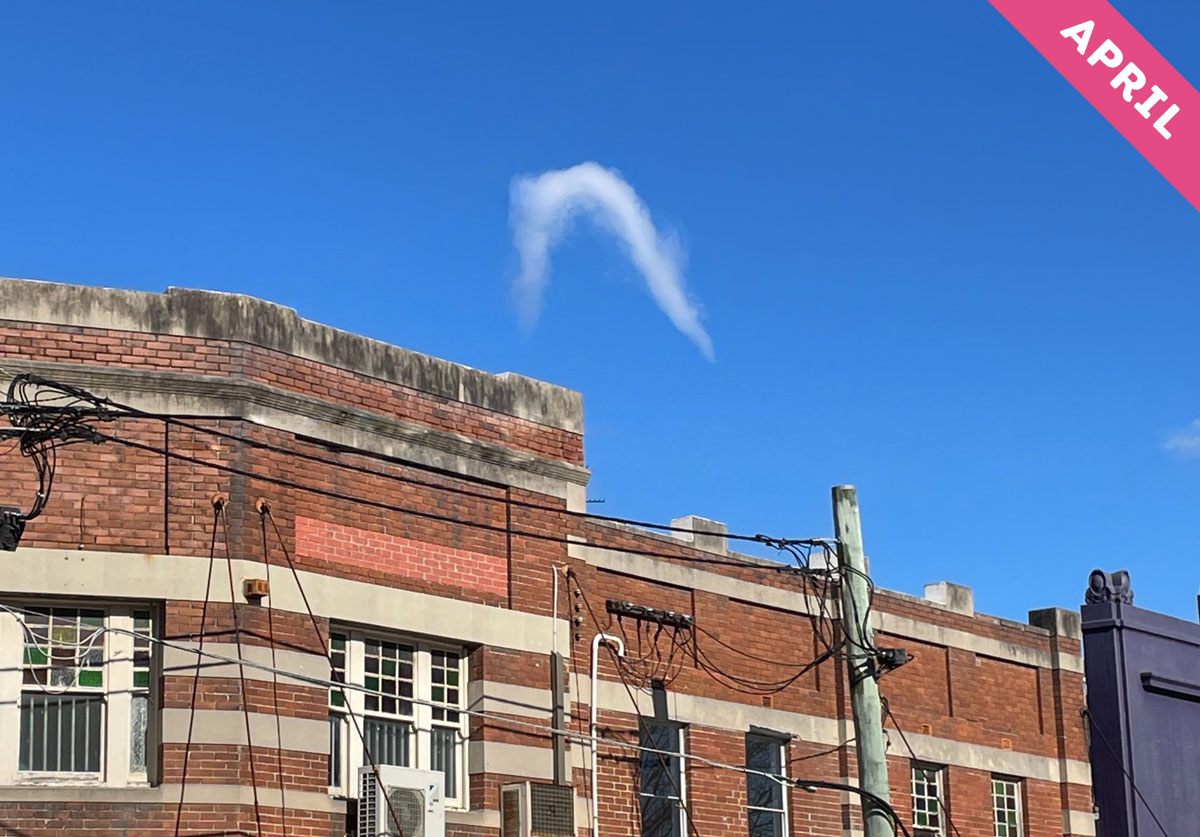
Cloud of the Month for April is the rare and fleeting horseshoe vortex cloud. Keen to spot one? Don’t get your hopes up…
Why do clouds sometimes line up in long, parallel streaks? We explain with the help of a cloud called Cirrus fibratus…
If ever there were a cloud forewarning of chaos, it would be the arcus, which features as Cloud of the Month for February…
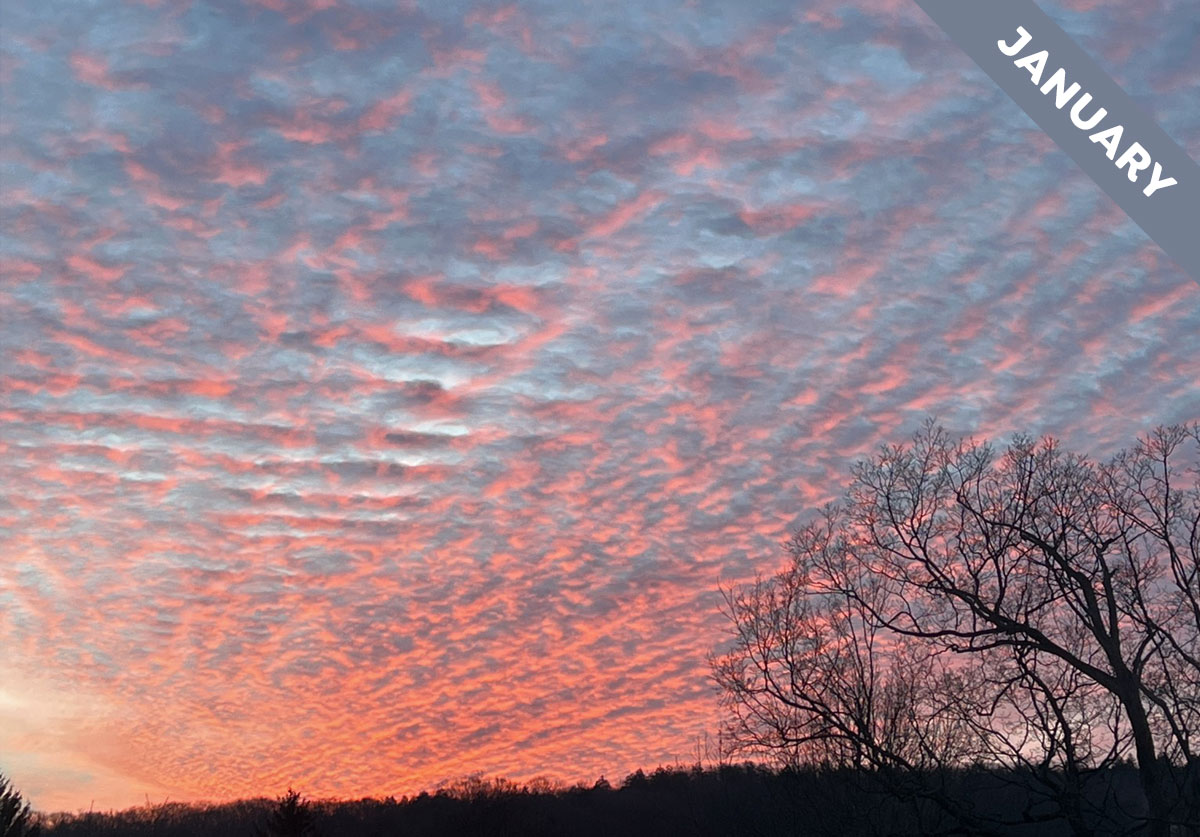
This form of Altocumulus cloud, spotted over Winsted, Connecticut, US by Pamela Crimmins (Member 48,931), reveals how the winds in our lower atmosphere can flow in different directions at different levels. We explain why in Cloud of the Month for January…
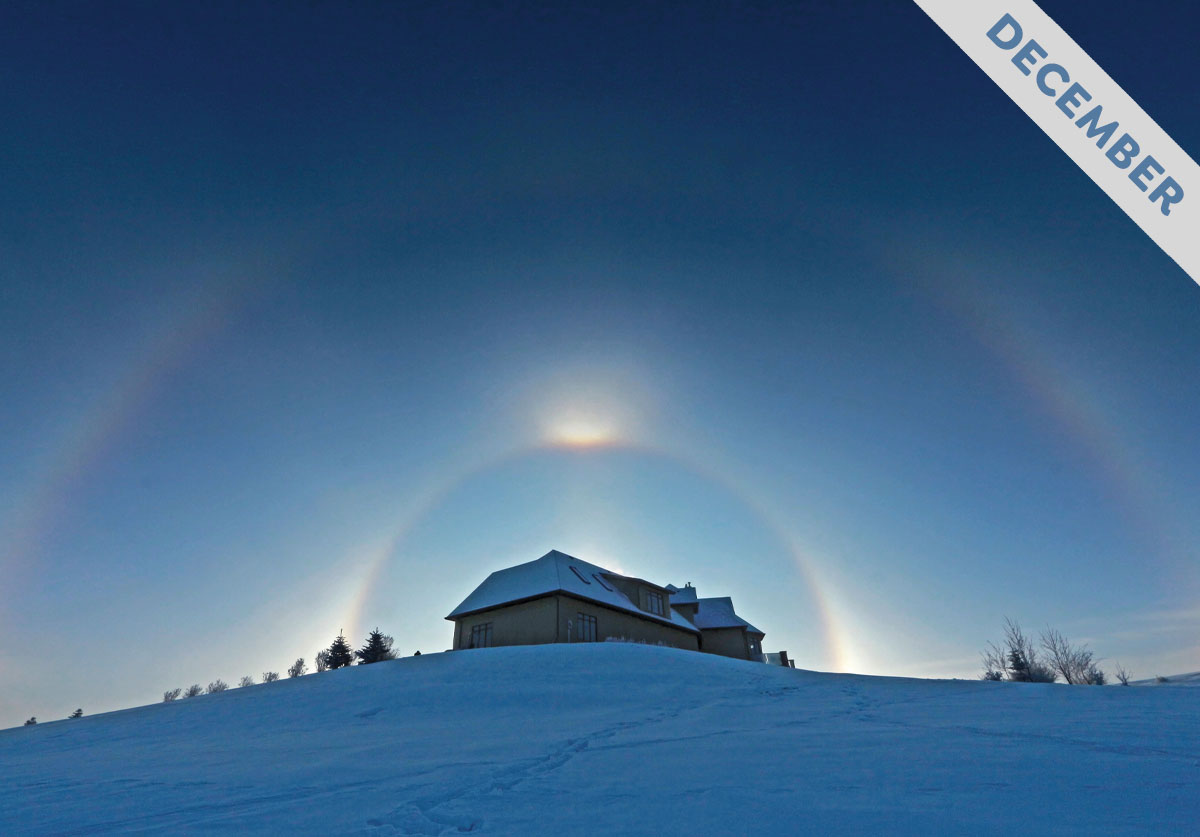
When you wake on a clear, freezing morning to sparkles in the sunlight and a host of bright arcs, rings and spots in the sky, you can thank the subtle ice fog known as diamond dust. This glittering morning mist plays the starring role in Cloud of the Month for December…
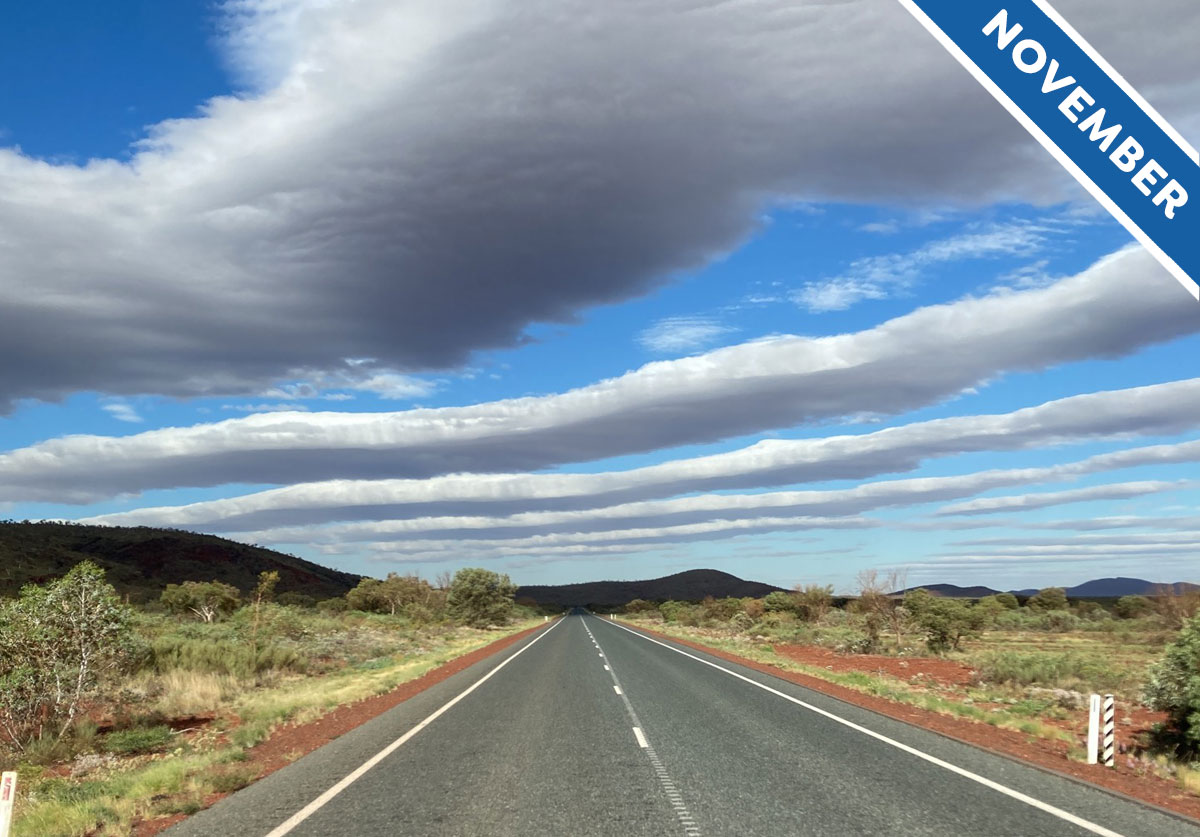
Meet the cloud formation that resembles those traffic safety markings on roads. We introduce Stratocumulus undulatus in Cloud of the Month for November…