Filter By:
Main Cloud Types
- Cumulus
- Stratus
- Stratocumulus
- Altocumulus
- Altostratus
- Cirrus
- Cirrocumulus
- Cirrostratus
- Nimbostratus
- Cumulonimbus
Other Clouds
- Arcus
- Asperitas
- Cap / banner clouds
- Capillatus
- Castellanus
- Cataractagenitus
- Cauda (Tail cloud)
- Cavum (Fallstreak hole)
- Congestus
- Contrail (homogenitus)
- Duplicatus
- Diamond dust
- Distrail
- Fibratus
- Flammagenitus (Pyrocumulus)
- Floccus
- Fluctus (Kelvin-Helmholtz)
- Fractus
- Homogenitus
- Horseshoe vortex
- Humilis
- Incus
- Intortus
- Lacunosus
- Lenticularis
- Mamma
- Morning Glory Cloud
- Murus (Wall cloud)
- Mediocris
- Nacreous
- Nebulosus
- Noctilucent
- Pannus
- Perlucidus
- Pileus
- Praecipitatio
- Radiatus
- Silvagenitus
- Spissatus
- Stratiformis
- 'Supercilium' (not official classification)
- Translucidus
- Tuba / Twister
- Uncinus
- Undulatus
- Velum
- Vertebratus
- Virga
- Volutus (Roll cloud)
Optical Effects
- 22° Halo
- 46° Halo
- Circumhorizon Arc
- Circumscribed halo
- Circumzenithal Arc
- Cloudbow / Fogbow
- Corona
- Crepuscular rays & shadows
- Diffuse arcs
- Green flash
- Glory
- Halos
- Helic arc
- Infralateral arc
- Iridescence
- Lower Sun Pillar
- Lower Tangent Arc
- Moonbow
- Moondogs
- Parhelic circle
- Parry antisolar arcs
- Parry arc
- Parry infralateral arc
- Parry supralateral arc
- Rainbow
- Sub parhelion
- Sub-sun
- Suncave parry arc
- Sun dog (Parhelion)
- Sun pillar
- Supernumerary bows
- Subparhelic circle
- Supralateral arc
- Upper tangent arc
- Wegener arc
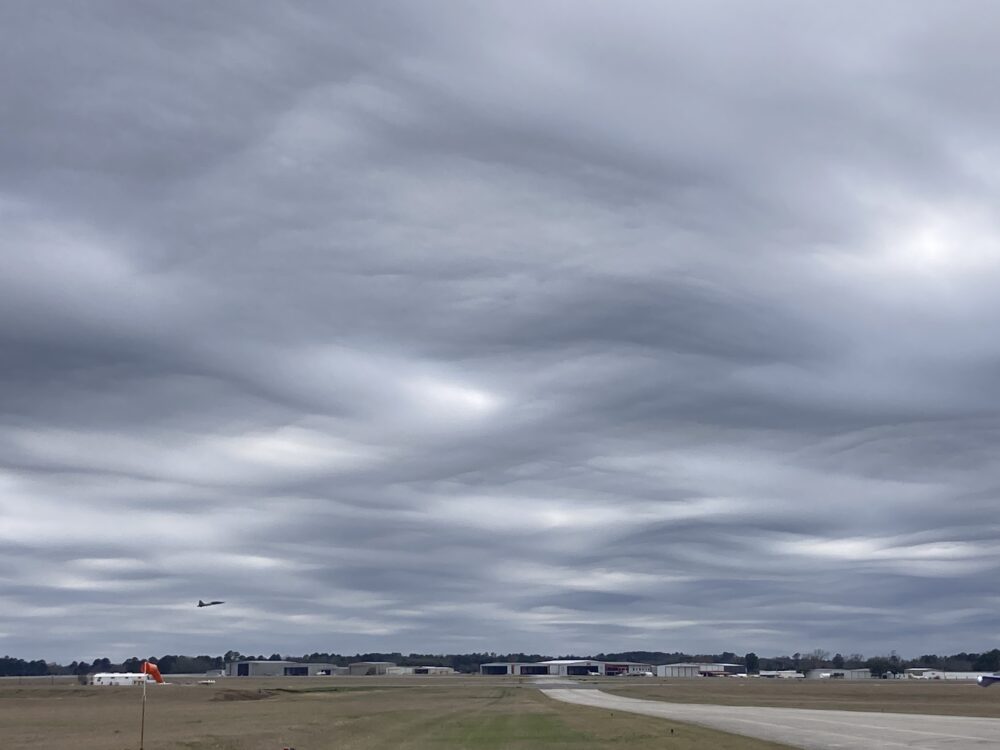
Asperitas spotted over East Texas Regional Airport, Longview, Texas, US
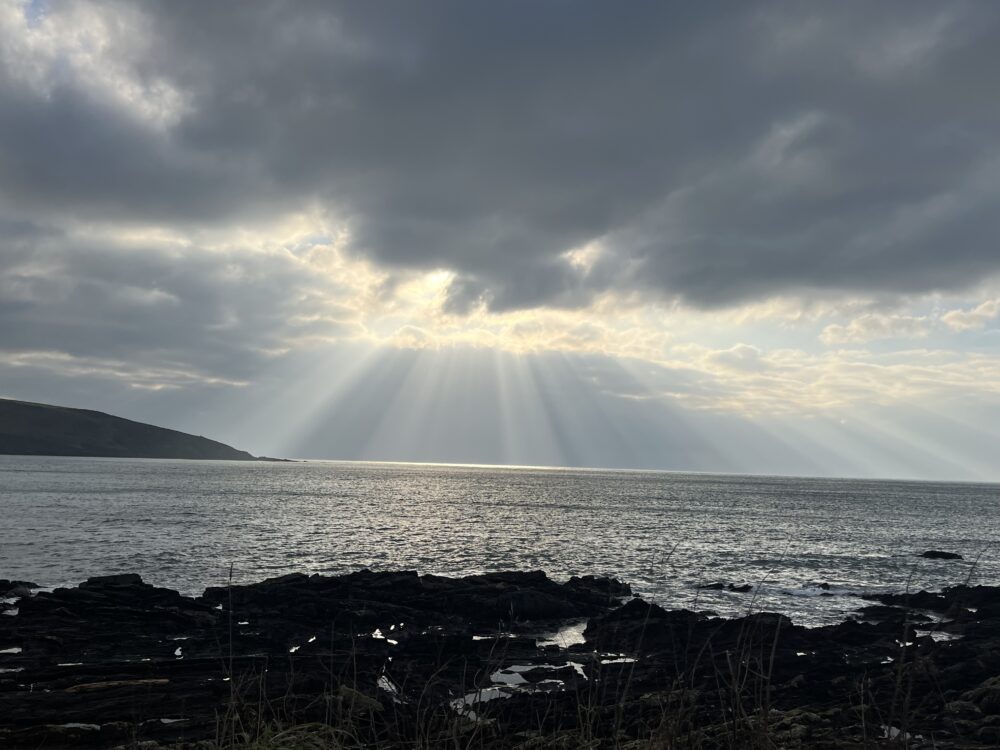
Crepuscular rays over Wembury Beach, Devon, England
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
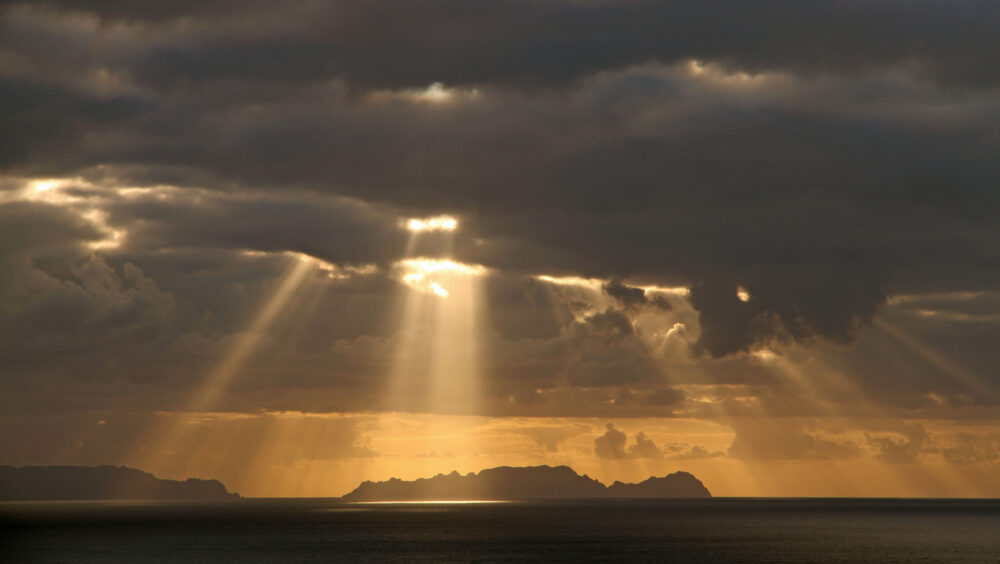
Crepuscular rays spotted over Funchal, Madeira, Portugal
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
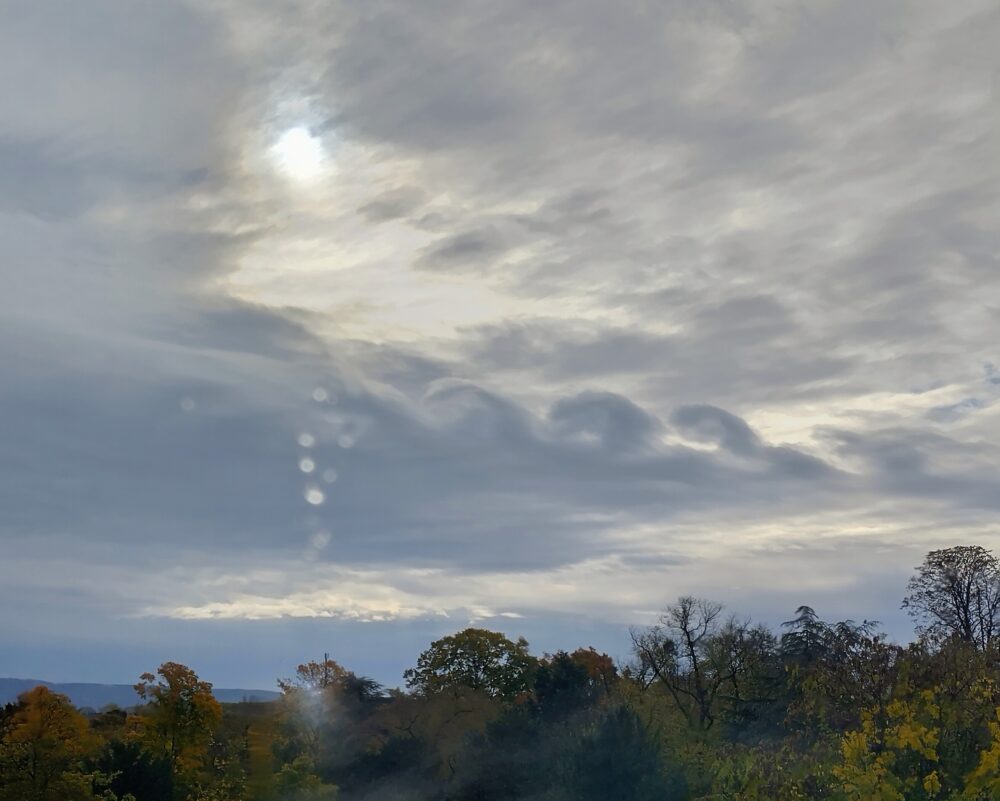
Fluctus (Kelvin-Helmholtz) spotted over Mannheim, Germany
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
A classic example of a rare horseshoe vortex spotted over Roanoke, Virginia, US
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Fallstreak Hole (Cavum) spotted over Conwy, North Wales
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
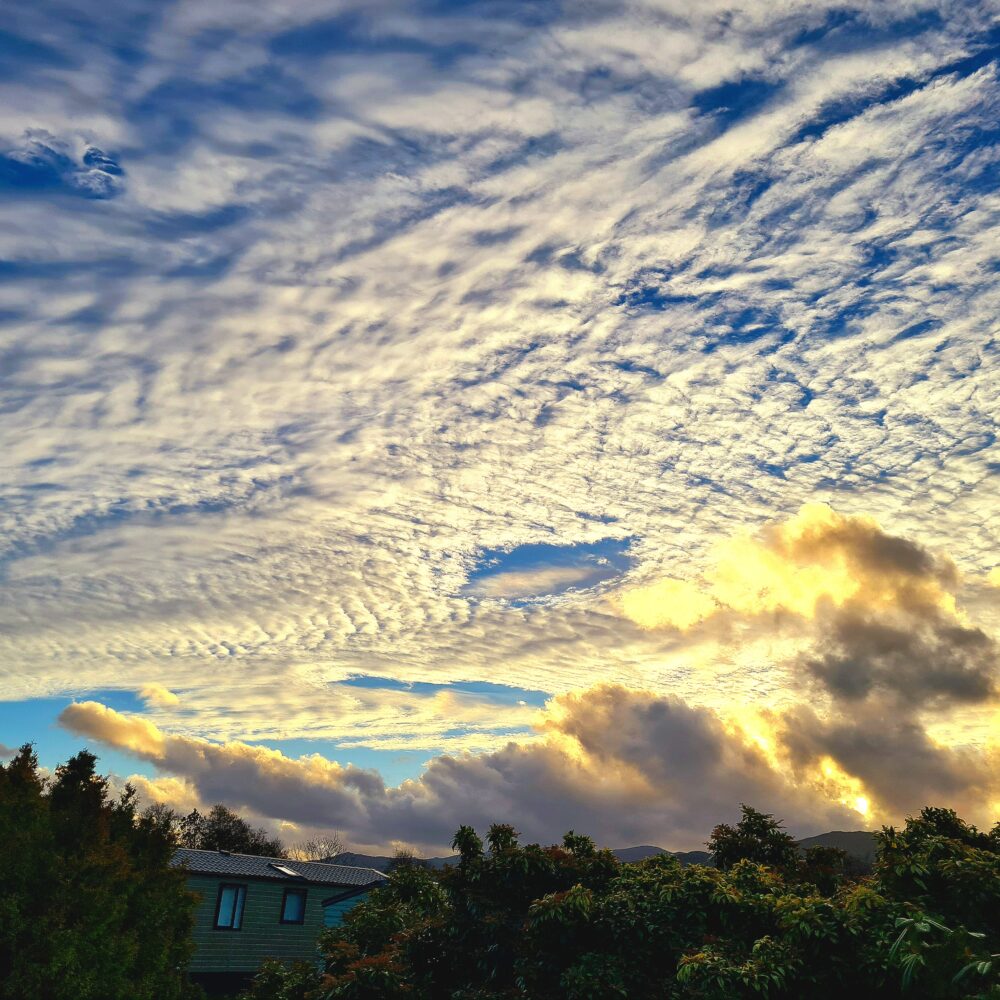
Altocumulus perlucidus spotted over Conwy, North Wales
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
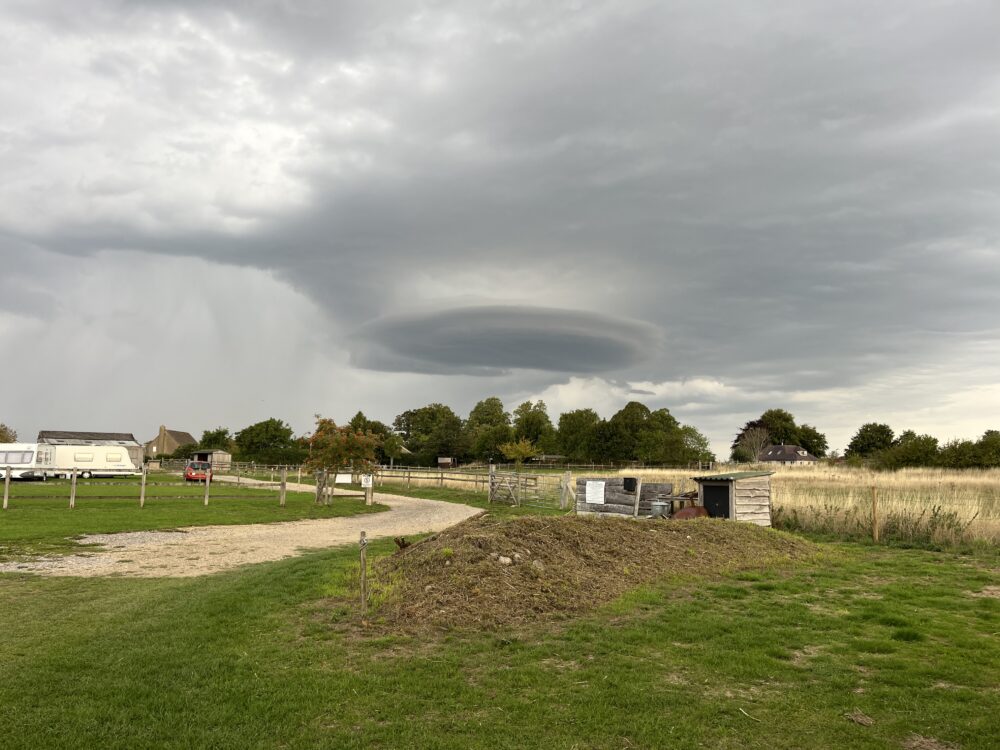
A low lying stratocumulus lenticularis spotted near Minchinhampton, Gloucestershire, England
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
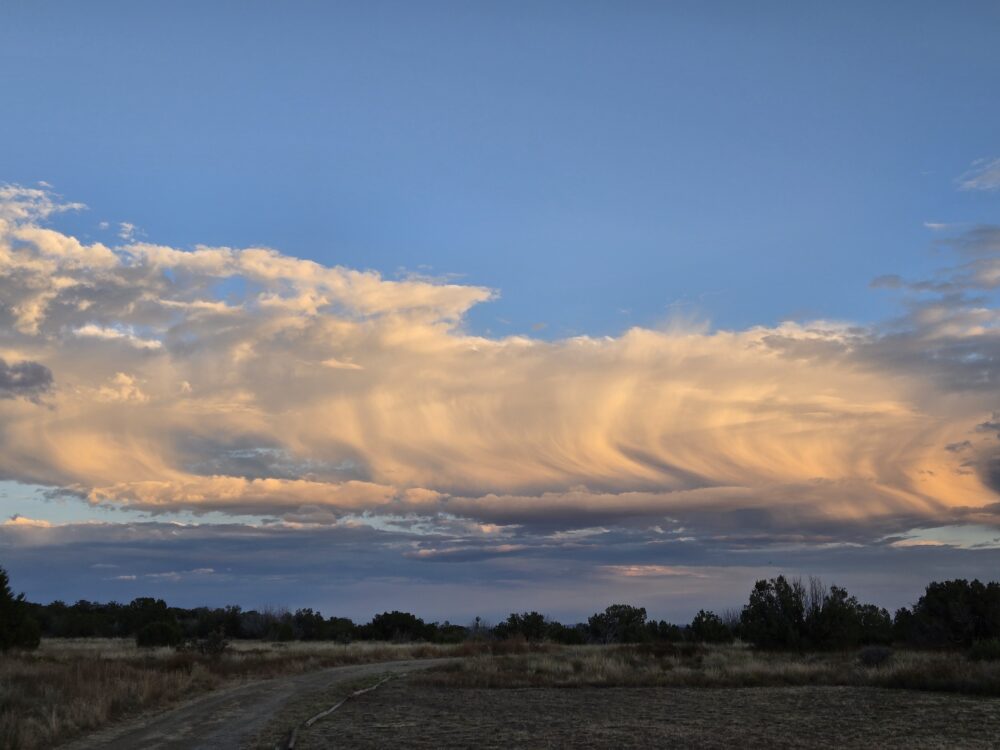
Taken during their daughter's wedding, an expansive view of virga was spotted near Santa Fe, New Mexico, US
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
A classic example of a distrail, also known as a dissipation trail, when a clear path is formed through a cloud by the passage of an airplane. It develops when the heat from an aircraft's engine warms and evaporates supercooled cloud droplets. This distrail, along with a nearby contrail, was spotted over Montmeló, Barcelona, Spain.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
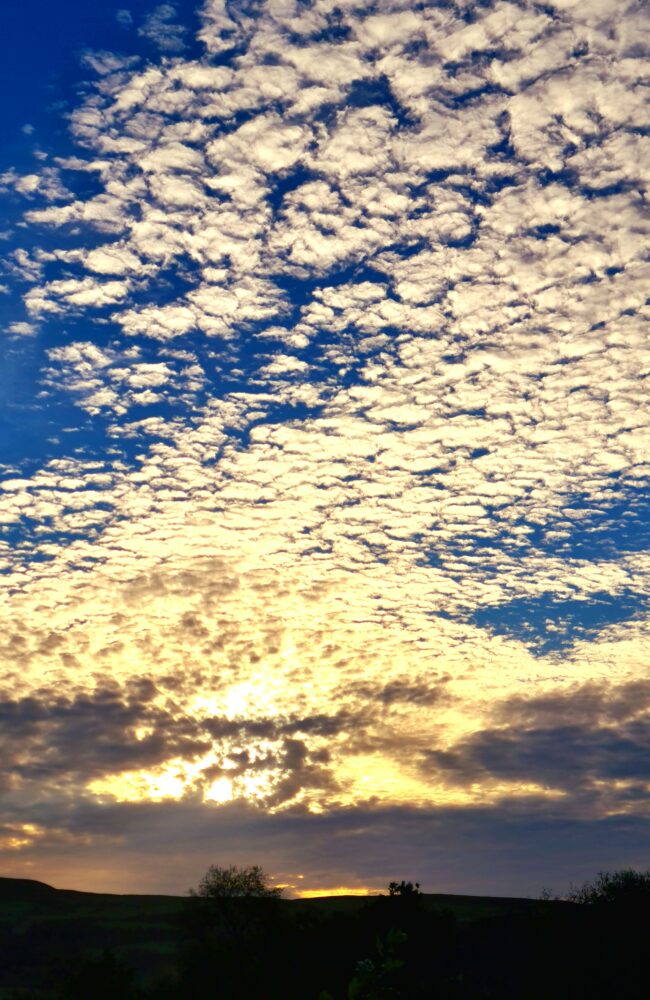
A blanket of stratocumulus over Puget Sound, Washington, US
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
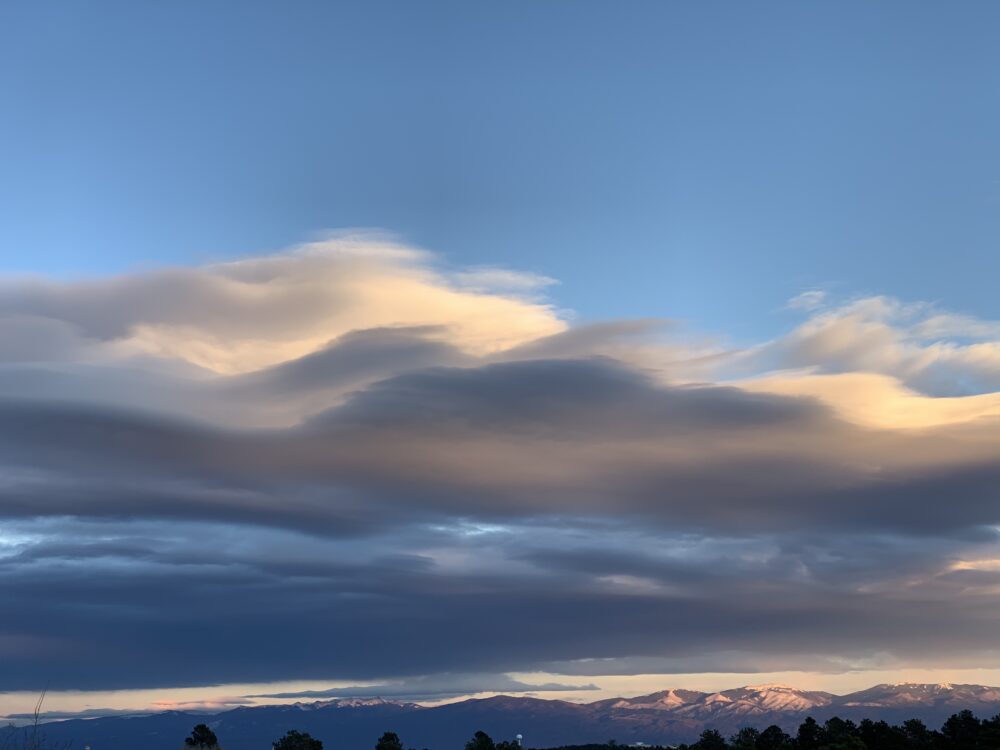
Altocumulus lenticularis spotted at sunset over the Sangre de Cristo Mountains north of Santa Fe, New Mexico, US
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
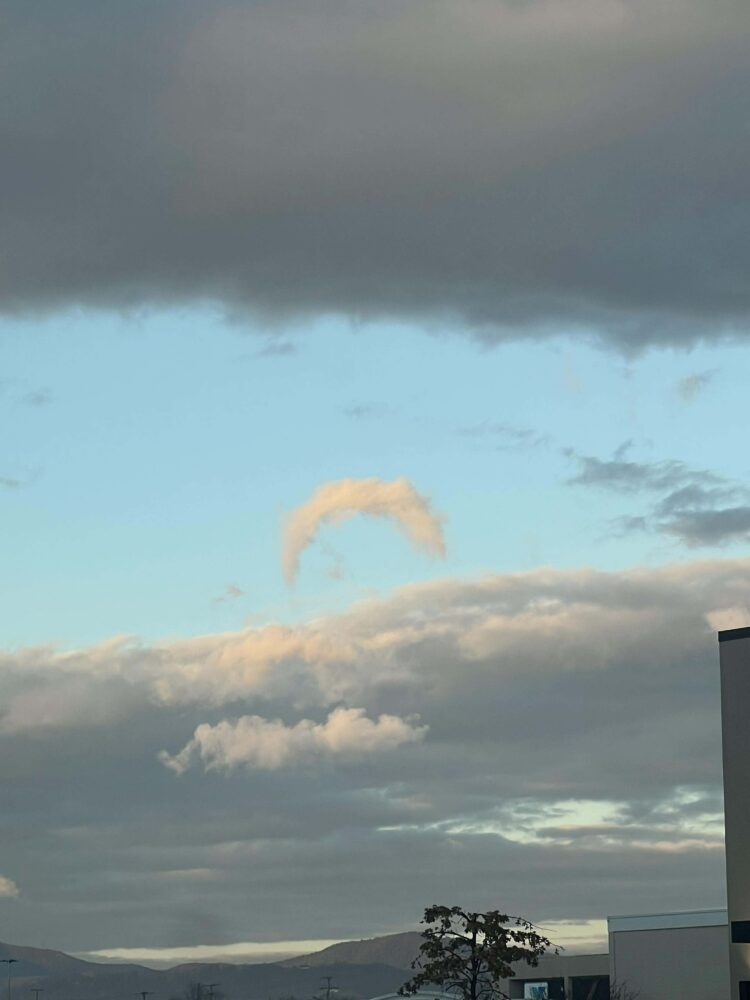
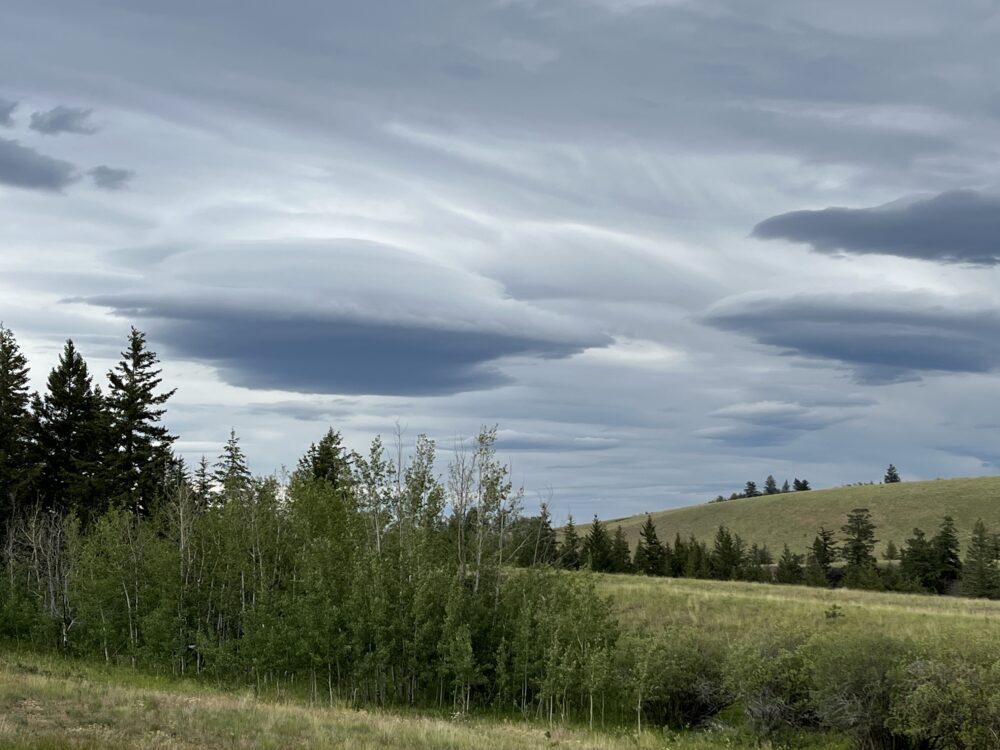
Stratocumulus lenticularis spotted over Kamloops, British Columbia, Canada
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
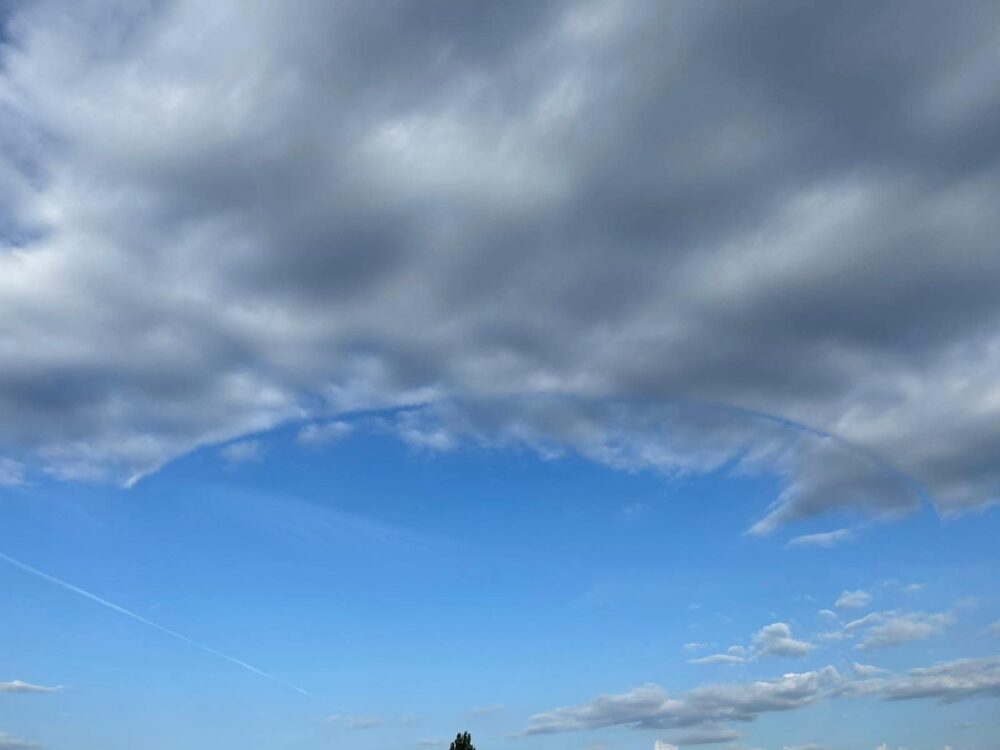
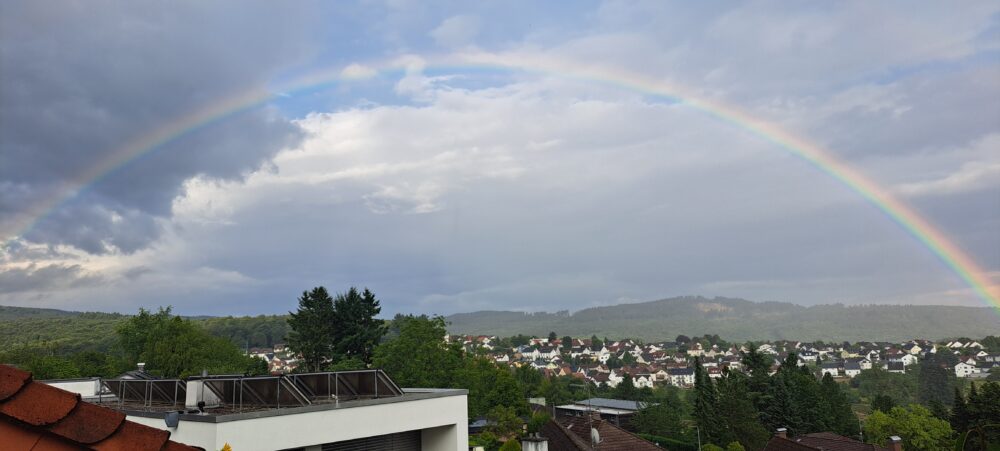
Rainbow over Schlossborn, Taunus, Germany
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Stratocumulus lenticularis, an uncommon version of the lenticular cloud, spotted over Avellino, Italy
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
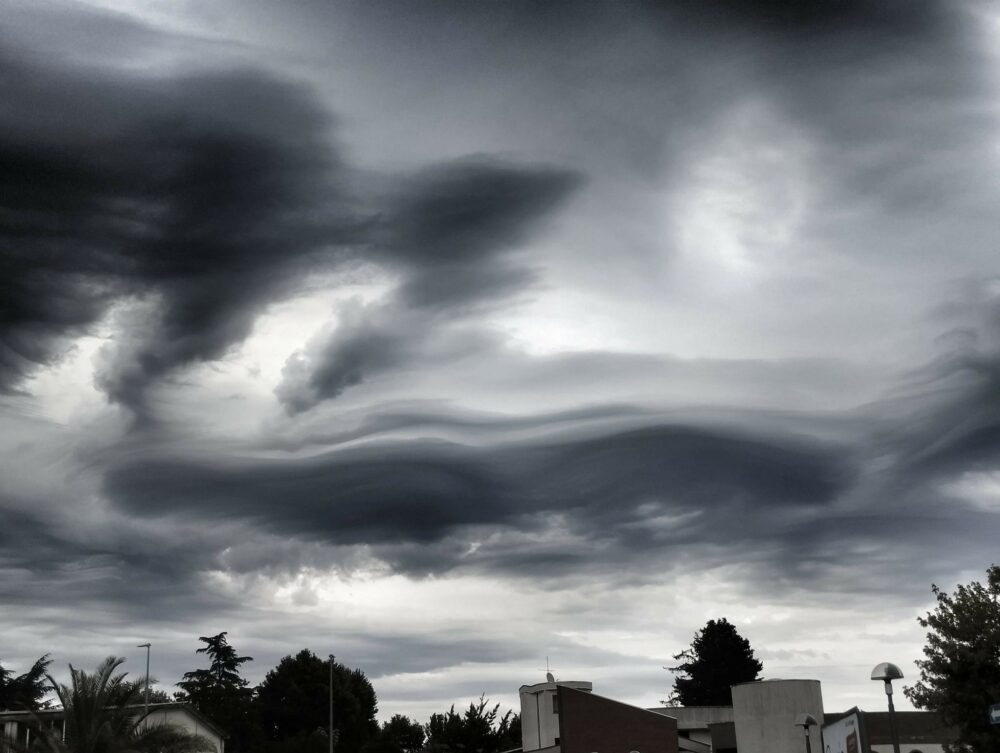
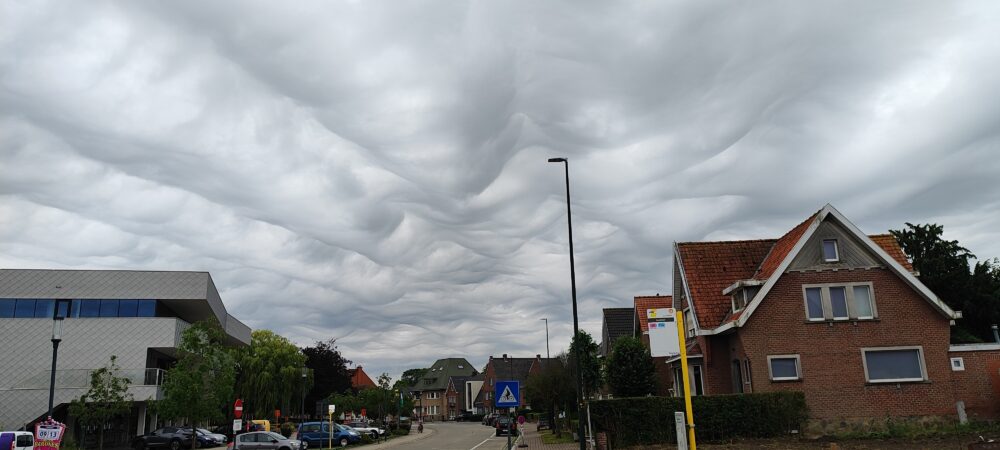
Asperitas over Torhout, West Flanders, Belgium
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.